Intro
Discover the evolution of logistics across four generations, from traditional transportation to modern digital ecosystems. Learn how changes in technology, consumer behavior, and global trade have shaped the industry, and explore the impact of emerging trends like e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) on logistics operations and supply chain management.
The logistics industry has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, and shifting market demands. In this article, we will explore the four generations of logistics, highlighting their key characteristics, benefits, and limitations. Understanding the evolution of logistics is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in today's fast-paced and competitive market.
The First Generation of Logistics: Physical Distribution (1950s-1970s)
The first generation of logistics focused on physical distribution, which involved the transportation of goods from one place to another. This era saw the rise of traditional logistics providers, such as trucking companies and warehouses. The primary goal was to move goods efficiently and effectively, with little emphasis on value-added services.
The First Generation of Logistics: Physical Distribution (1950s-1970s)

The second generation of logistics emerged in the 1980s, with a focus on integrated logistics. This era saw the rise of third-party logistics (3PL) providers, who offered a range of services, including transportation, warehousing, and freight forwarding.
The Second Generation of Logistics: Integrated Logistics (1980s-1990s)

The Third Generation of Logistics: Global Logistics (2000s-2010s)
The third generation of logistics focused on global logistics, with the rise of globalization and international trade. This era saw the emergence of fourth-party logistics (4PL) providers, who offered end-to-end supply chain solutions.
The Third Generation of Logistics: Global Logistics (2000s-2010s)

The fourth generation of logistics is focused on digital logistics, with the rise of e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This era has seen the emergence of digital logistics platforms, which offer real-time visibility, data analytics, and automation.
The Fourth Generation of Logistics: Digital Logistics (2020s-present)

Key Characteristics of Each Generation
Each generation of logistics has its unique characteristics, benefits, and limitations. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in today's fast-paced and competitive market.
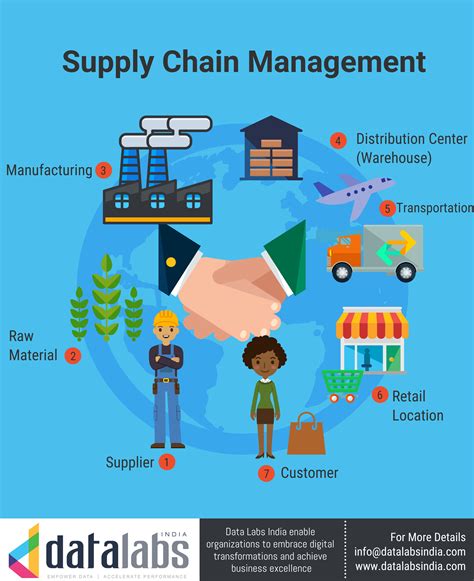
- Physical Distribution (1950s-1970s): Focus on transportation, warehousing, and freight forwarding. Benefits: efficient movement of goods, limited value-added services. Limitations: lack of visibility, limited scalability.
- Integrated Logistics (1980s-1990s): Focus on integrated services, including transportation, warehousing, and freight forwarding. Benefits: end-to-end solutions, improved visibility, increased scalability. Limitations: limited technology adoption, high costs.
- Global Logistics (2000s-2010s): Focus on global supply chain solutions, including 4PL providers. Benefits: end-to-end solutions, improved visibility, increased scalability, global reach. Limitations: high costs, complex operations.
- Digital Logistics (2020s-present): Focus on digital platforms, real-time visibility, data analytics, and automation. Benefits: real-time visibility, improved efficiency, increased scalability, reduced costs. Limitations: high technology adoption costs, cybersecurity risks.
Best Practices for Implementing Digital Logistics
Implementing digital logistics requires a strategic approach, including:
- Assessing current operations: Evaluate existing logistics operations, identifying areas for improvement and opportunities for digitalization.
- Defining digitalization goals: Establish clear goals for digitalization, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experience.
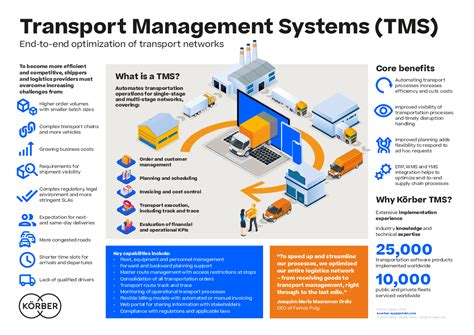
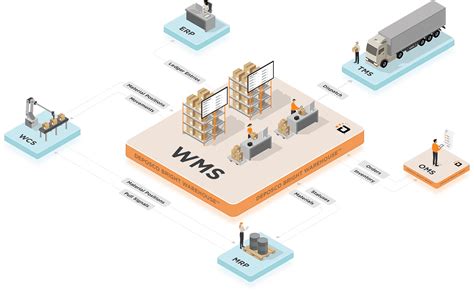
- Selecting digital platforms: Choose digital platforms that align with business goals, including transportation management systems, warehouse management systems, and data analytics tools.
- Developing a change management plan: Create a plan to manage change, including training employees, updating processes, and monitoring progress.
- Ensuring cybersecurity: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and cyber threats.
Conclusion
The logistics industry has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, and shifting market demands. Understanding the four generations of logistics is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in today's fast-paced and competitive market. By adopting digital logistics, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experience.
Gallery of Logistics
Logistics Image Gallery







FAQs
What is the difference between traditional logistics and digital logistics?
+Traditional logistics focuses on physical distribution, while digital logistics focuses on digital platforms, real-time visibility, data analytics, and automation.
What are the benefits of implementing digital logistics?
+The benefits of implementing digital logistics include improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced customer experience, and increased scalability.
What are the best practices for implementing digital logistics?
+The best practices for implementing digital logistics include assessing current operations, defining digitalization goals, selecting digital platforms, developing a change management plan, and ensuring cybersecurity.
