Intro
Discover the pivotal 5 roles of an Air Battle Manager, expertly orchestrating combat operations from planning to execution. Learn how they integrate command, control, and communication to deliver strategic air power, ensuring mission success in dynamic, high-pressure environments, with a focus on tactical expertise, situational awareness, and decisive decision-making.
Air Battle Managers (ABMs) play a critical role in the military, particularly in the air force, where they are responsible for directing and controlling air operations to achieve strategic objectives. Their work is multifaceted, requiring a deep understanding of air power, communication skills, and the ability to make quick decisions in high-pressure situations. Here, we delve into five key roles of an Air Battle Manager, exploring their responsibilities, skills, and the impact they have on military operations.
Role 1: Air Mission Planning and Execution

Air Battle Managers are involved in the planning and execution of air missions. This involves working closely with pilots, intelligence officers, and other stakeholders to plan and coordinate air sorties. They must have a detailed understanding of the air power capabilities, including the types of aircraft available, their performance characteristics, and the armaments they can carry. ABMs must also be aware of the operational environment, including weather conditions, enemy defenses, and potential risks to friendly forces.
During the execution phase, ABMs monitor the progress of air missions, providing real-time guidance to pilots and responding to changing circumstances. This might involve re-tasking aircraft, adjusting routes to avoid enemy fire, or coordinating with other units to ensure a unified response.
Role 2: Situational Awareness and Battle Management
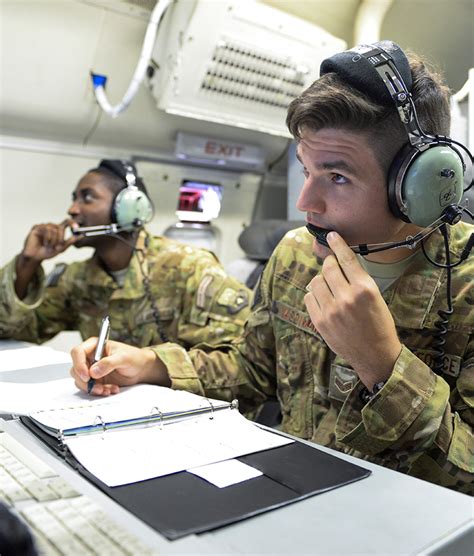
ABMs must maintain situational awareness of the operational environment, tracking the location and status of friendly and enemy forces. This involves analyzing data from a variety of sources, including radar, intelligence reports, and communication from pilots. By maintaining a clear picture of the battlefield, ABMs can make informed decisions about how to allocate air assets, prioritize targets, and respond to emerging threats.
Battle management involves directing air operations to achieve strategic objectives. This might involve coordinating with other branches of the military, such as ground forces or naval units, to ensure a unified response. ABMs must be able to think critically and make quick decisions in high-pressure situations, often with limited information.
Key Skills for Situational Awareness and Battle Management
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Ability to think critically and make quick decisions
- Excellent communication and coordination skills
- Familiarity with air power capabilities and operational procedures
Role 3: Communication and Coordination

Effective communication and coordination are critical components of the ABM role. They must be able to clearly articulate instructions and guidance to pilots, as well as coordinate with other units and stakeholders to ensure a unified response. This involves working with a range of communication systems, including radios, data links, and voice-over-internet protocol (VOIP) systems.
ABMs must also be able to receive and process information from a variety of sources, including pilots, intelligence reports, and other units. This requires strong listening and comprehension skills, as well as the ability to filter out irrelevant information and focus on key details.
Key Skills for Communication and Coordination
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Ability to work effectively in a team environment
- Strong listening and comprehension skills
- Familiarity with communication systems and protocols
Role 4: Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) Management

ABMs play a critical role in managing ISR assets, including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), satellites, and manned reconnaissance aircraft. They must be able to task and coordinate these assets to gather critical information about the operational environment, including enemy troop movements, defensive positions, and potential targets.
ISR management involves analyzing data from a range of sources, including sensors, cameras, and human intelligence. ABMs must be able to filter out irrelevant information, identify key trends and patterns, and provide actionable intelligence to commanders and pilots.
Key Skills for ISR Management
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Familiarity with ISR systems and capabilities
- Ability to think critically and make informed decisions
- Excellent communication and coordination skills
Role 5: Training and Development

Finally, ABMs play a critical role in training and developing junior personnel. They must be able to teach and mentor others in the skills and knowledge required to perform the ABM role, including air mission planning, battle management, and ISR management.
Training and development involve creating and delivering instructional programs, as well as providing on-the-job training and feedback. ABMs must be able to assess the performance of junior personnel, identify areas for improvement, and provide constructive feedback and guidance.
Key Skills for Training and Development
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Ability to teach and mentor others
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Familiarity with training and development methodologies
Air Battle Manager Image Gallery





What is the role of an Air Battle Manager?
+An Air Battle Manager is a critical component of air operations, responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing air missions to achieve strategic objectives.
What skills are required to be a successful Air Battle Manager?
+A successful Air Battle Manager requires strong analytical and problem-solving skills, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, and the ability to think critically and make informed decisions.
What is the importance of situational awareness in air operations?
+Situational awareness is critical in air operations, as it enables Air Battle Managers to maintain a clear picture of the operational environment, track the location and status of friendly and enemy forces, and make informed decisions about how to allocate air assets.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the critical role of Air Battle Managers in modern air operations. By understanding the skills, responsibilities, and challenges associated with this role, we can better appreciate the importance of effective air mission planning, execution, and management in achieving strategic objectives. If you have any further questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out.
