Intro
Discover the pivotal moments that defined Americas history in 10 Moments That Shaped The Annals Of America. From revolutionary wars to social movements, explore the key events, milestones, and cultural shifts that transformed the nation, including colonial expansion, civil rights, and technological advancements that forged the countrys identity.
The United States of America has a rich and diverse history, spanning over two centuries. From the early colonial days to the present, the country has experienced numerous events that have shaped its development, politics, and culture. Here are 10 moments that have significantly impacted the annals of America.

The signing of the Declaration of Independence in 1776 marked the beginning of the American Revolution, as the colonies sought to break free from British rule. This pivotal moment not only declared the 13 colonies as independent states but also established the principles of liberty and democracy that would shape the nation's future.
The American Revolution and Its Aftermath
The American Revolution, which lasted from 1775 to 1783, was a defining moment in American history. The war not only secured independence from Britain but also laid the foundation for the United States' government and political system. The Revolutionary War was fought on multiple fronts, with key battles taking place in Lexington and Concord, Bunker Hill, and Yorktown.

The Revolution's aftermath saw the drafting of the United States Constitution in 1787, which established the framework for the federal government and the relationship between the government and the citizens. The Constitution's ratification in 1788 marked the beginning of the United States as a sovereign nation.
The Civil War and Reconstruction
The American Civil War, fought between 1861 and 1865, was a brutal and devastating conflict that tested the nation's unity and values. The war was sparked by the secession of 11 Southern states, which sought to preserve the institution of slavery. The Union, led by President Abraham Lincoln, ultimately prevailed, but not before the war had claimed the lives of an estimated 620,000 to 750,000 soldiers and civilians.

The Reconstruction Era, which followed the Civil War, aimed to rebuild the nation and ensure the rights of formerly enslaved individuals. The period saw the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution, which abolished slavery, granted citizenship to African Americans, and protected their right to vote.
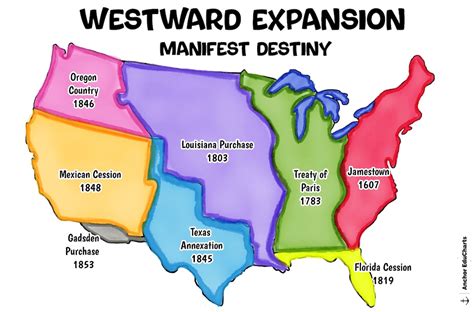
Westward Expansion and the Industrial Revolution
The late 19th century saw a period of rapid expansion and industrialization in the United States. The construction of the transcontinental railroad in 1869 facilitated westward expansion, as thousands of settlers moved to the American West in search of land, gold, and opportunity.
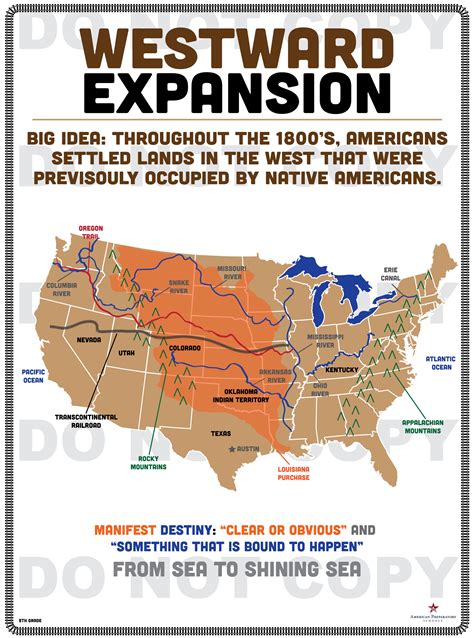
The Industrial Revolution transformed the nation's economy, as new technologies and manufacturing techniques enabled mass production and increased efficiency. The period saw the rise of industrialists such as Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, and J.P. Morgan, who built vast fortunes and shaped the nation's economy.
World War I and the Roaring Twenties
The United States' entry into World War I in 1917 marked a significant turning point in the nation's history. The war saw the introduction of new technologies, including tanks, airplanes, and machine guns, which transformed modern warfare.

The post-war period saw a cultural and economic shift, as the Roaring Twenties brought a sense of liberation and excess. The Harlem Renaissance, led by writers such as Langston Hughes and Zora Neale Hurston, celebrated African American culture and identity.
The Great Depression and World War II
The stock market crash of 1929 marked the beginning of the Great Depression, a period of economic downturn that lasted over a decade. The Depression saw widespread unemployment, poverty, and social unrest, but also spurred the development of new economic policies and social programs.

The United States' entry into World War II in 1941 marked a turning point in the nation's history. The war saw the mobilization of the American economy and the deployment of millions of soldiers abroad. The war's aftermath saw the emergence of the United States as a global superpower.
The Civil Rights Movement
The Civil Rights Movement of the 1950s and 1960s aimed to end racial segregation and discrimination in the United States. Led by figures such as Martin Luther King Jr., Rosa Parks, and Malcolm X, the movement saw significant victories, including the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.

The movement also saw violent confrontations, including the bombing of the 16th Street Baptist Church in Birmingham, Alabama, and the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in Memphis, Tennessee.
The Vietnam War and the Counterculture
The United States' involvement in the Vietnam War, which lasted from 1955 to 1975, was a divisive and unpopular conflict. The war saw widespread protests and social unrest, as many Americans questioned the nation's involvement in the conflict.

The counterculture movement of the 1960s and 1970s saw a rejection of mainstream values and the emergence of new social and cultural norms. The movement celebrated free love, rock music, and alternative lifestyles, but also saw the rise of new social and environmental concerns.
The Fall of the Berlin Wall and the End of the Cold War
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked the beginning of the end of the Cold War, a decades-long conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union. The event saw the reunification of Germany and the collapse of communist regimes across Eastern Europe.

The aftermath of the Cold War saw a new era of international relations, as the United States emerged as the world's sole superpower. The period also saw the rise of new global challenges, including terrorism, climate change, and economic inequality.
Gallery of American History
American History Image Gallery









What was the significance of the American Revolution?
+The American Revolution marked the beginning of the United States' independence from Britain and established the principles of liberty and democracy that would shape the nation's future.
What were the main causes of the Civil War?
+The main causes of the Civil War included the issue of slavery, states' rights, and economic and cultural differences between the North and South.
What was the significance of the Civil Rights Movement?
+The Civil Rights Movement aimed to end racial segregation and discrimination in the United States, achieving significant victories, including the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
