Intro
Discover the perfect hues for your next art project with our guide to 7 essential colour palettes for painting. From bold and bright to soft and subtle, explore a range of harmonious colour combinations, including complementary, analogous, and triadic palettes, to elevate your artwork and evoke emotions.
Colour palettes are a crucial aspect of painting, as they can evoke emotions, create moods, and convey messages. A well-chosen colour palette can make or break a painting, and artists often spend a significant amount of time selecting the perfect colours for their work. In this article, we will explore seven essential colour palettes for painting, including their characteristics, uses, and examples of how they can be applied in art.

1. The Primary Colour Palette
The primary colour palette consists of the three fundamental colours: red, yellow, and blue. These colours cannot be created by mixing other colours together, and they are the base colours used to create all other colours. The primary colour palette is versatile and can be used to create a wide range of moods and effects.
Characteristics:
- Bright and vibrant colours
- Can be used to create bold and dramatic effects
- Suitable for abstract, expressionist, and pop art styles
Examples:
- Mark Rothko's "No. 61 (Rust and Blue)" (1953)
- Piet Mondrian's "Composition with Red, Yellow, and Blue" (1921)

2. The Monochromatic Colour Palette
A monochromatic colour palette consists of different shades of the same colour. This palette is ideal for creating subtle, nuanced, and cohesive artworks. Monochromatic colour schemes can be used to evoke emotions and create a sense of depth and atmosphere.
Characteristics:
- Different shades of the same colour
- Creates a cohesive and harmonious effect
- Suitable for landscape, still life, and portrait painting
Examples:
- Claude Monet's "Impression, Sunrise" (1872)
- Andrew Wyeth's "Christina's World" (1948)

3. The Complementary Colour Palette
The complementary colour palette consists of pairs of colours that are opposite each other on the colour wheel. This palette is ideal for creating bold, vibrant, and contrasting artworks. Complementary colours can be used to evoke emotions and create a sense of tension and drama.
Characteristics:
- Pairs of colours that are opposite each other on the colour wheel
- Creates a bold and vibrant effect
- Suitable for abstract, expressionist, and pop art styles
Examples:
- Vincent van Gogh's "The Starry Night" (1889)
- Pablo Picasso's "Guernica" (1937)

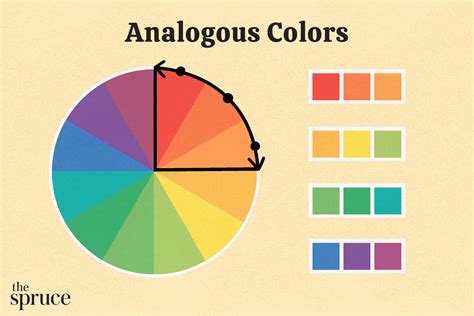
4. The Analogous Colour Palette
The analogous colour palette consists of colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel. This palette is ideal for creating smooth, harmonious, and cohesive artworks. Analogous colours can be used to evoke emotions and create a sense of depth and atmosphere.
Characteristics:
- Colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel
- Creates a smooth and harmonious effect
- Suitable for landscape, still life, and portrait painting
Examples:
- Claude Monet's "Water Lilies" (1916-1926)
- Johannes Vermeer's "Girl with a Pearl Earring" (1665)
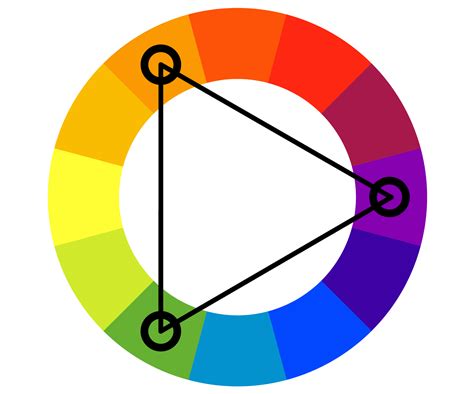
5. The Triadic Colour Palette
The triadic colour palette consists of three colours that are equally spaced from each other on the colour wheel. This palette is ideal for creating bold, vibrant, and contrasting artworks. Triadic colours can be used to evoke emotions and create a sense of tension and drama.
Characteristics:
- Three colours that are equally spaced from each other on the colour wheel
- Creates a bold and vibrant effect
- Suitable for abstract, expressionist, and pop art styles
Examples:
- Wassily Kandinsky's "Composition VIII" (1923)
- Kazimir Malevich's "Black Square" (1915)
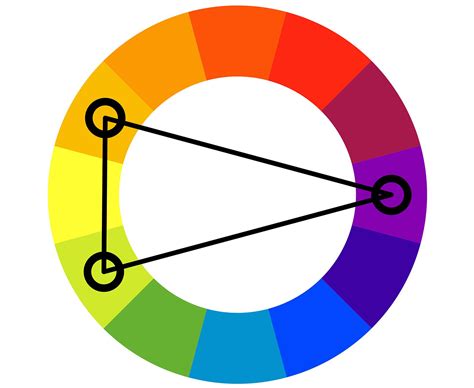
6. The Split-Complementary Colour Palette
The split-complementary colour palette consists of a colour and the two colours on either side of its complementary colour. This palette is ideal for creating bold, vibrant, and contrasting artworks. Split-complementary colours can be used to evoke emotions and create a sense of tension and drama.
Characteristics:
- A colour and the two colours on either side of its complementary colour
- Creates a bold and vibrant effect
- Suitable for abstract, expressionist, and pop art styles
Examples:
- Paul Klee's "Ancient Harmony" (1925)
- Franz Marc's "The Blue Horse" (1911)
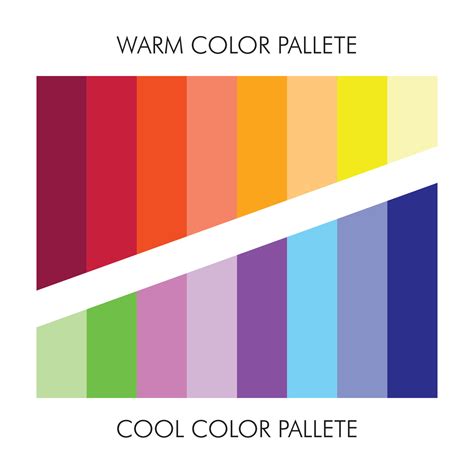
7. The Warm and Cool Colour Palette
The warm and cool colour palette consists of colours that are divided into warm and cool categories. Warm colours, such as red, orange, and yellow, evoke emotions and create a sense of warmth and energy. Cool colours, such as blue, green, and purple, evoke emotions and create a sense of calmness and serenity.
Characteristics:
- Colours divided into warm and cool categories
- Warm colours evoke emotions and create a sense of warmth and energy
- Cool colours evoke emotions and create a sense of calmness and serenity
- Suitable for landscape, still life, and portrait painting
Examples:
- Vincent van Gogh's "Sunflowers" (1888)
- Claude Monet's "Impression, Sunrise" (1872)

Gallery of Colour Palettes:
Colour Palette Gallery









What is a colour palette?
+A colour palette is a selection of colours used in a painting or artwork to create a specific mood, atmosphere, or effect.
How do I choose a colour palette for my painting?
+Choose a colour palette that complements the theme, subject, and mood of your painting. Consider the emotions and atmosphere you want to evoke, and select colours that will achieve that effect.
What are the most common colour palettes used in painting?
+The most common colour palettes used in painting include the primary colour palette, monochromatic colour palette, complementary colour palette, analogous colour palette, triadic colour palette, split-complementary colour palette, and warm and cool colour palette.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the seven essential colour palettes for painting. By selecting the right colour palette for your artwork, you can evoke emotions, create moods, and convey messages that will engage and inspire your audience.
