Intro
Discover why cold air sinks in this in-depth exploration of atmospheric science. Learn about the 5 key reasons behind this phenomenon, including density, gravity, and heat transfer. Understand the role of temperature, air pressure, and convection in shaping our climate. Get the facts on why cold air behaves the way it does.
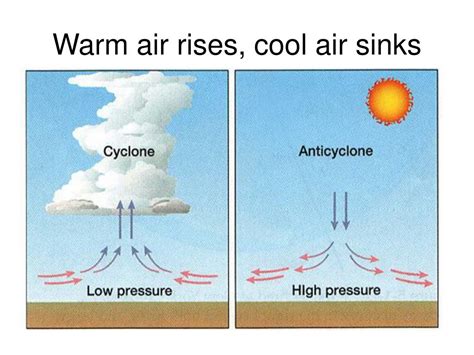
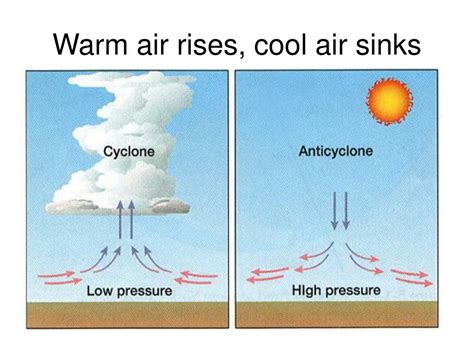
As we all know, warm air rises and cool air sinks. But have you ever stopped to think about why this is the case? The concept of air movement is crucial in understanding various weather phenomena, from gentle breezes to powerful storms. In this article, we will delve into the five main reasons why cold air sinks.
Understanding the Basics of Air Movement

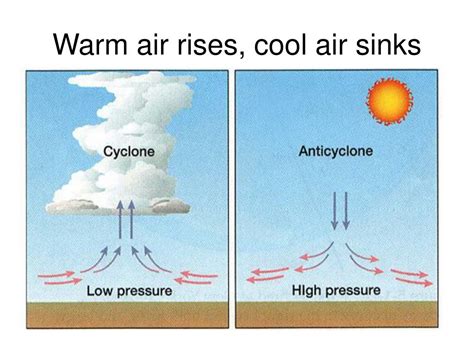
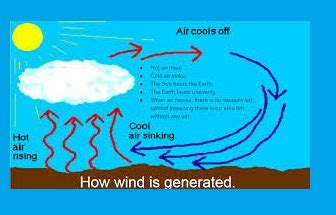
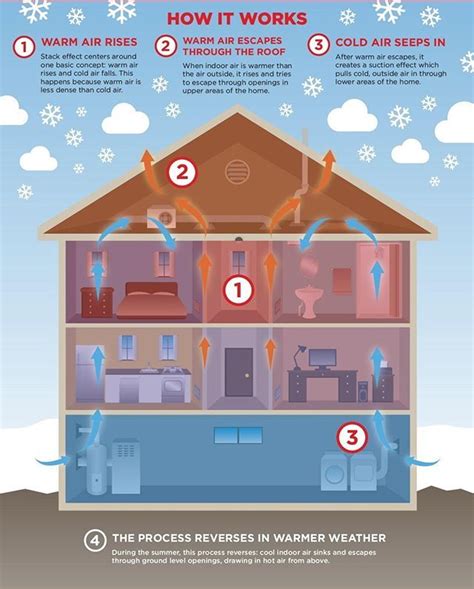
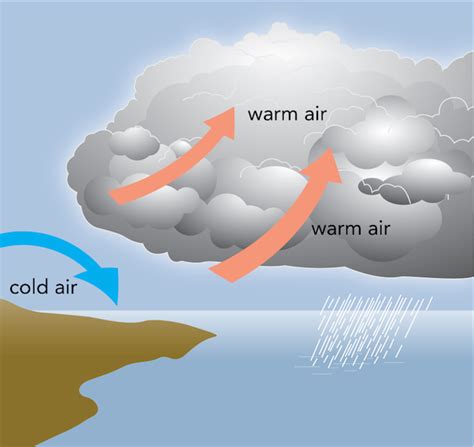
Before we dive into the reasons why cold air sinks, it's essential to understand the basics of air movement. Air is made up of various gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. When the sun heats the Earth's surface, it warms the air closest to the ground, causing it to expand and rise. This creates an area of low pressure near the ground, which pulls in more air to replace the rising air. As the air rises, it cools, and its ability to hold moisture decreases, resulting in the formation of clouds and precipitation.
Reason 1: Density
One of the primary reasons why cold air sinks is due to its density. Cold air is denser than warm air, meaning it has a higher mass per unit volume. This is because cold air molecules are closer together and move more slowly than warm air molecules. As a result, cold air is heavier than warm air and tends to sink to the ground.
Reason 2: Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in air movement. When air is heated, it expands and becomes less dense, causing it to rise. Conversely, when air is cooled, it contracts and becomes denser, causing it to sink. This is why cold air tends to sink towards the ground, while warm air rises.
Reason 3: Humidity
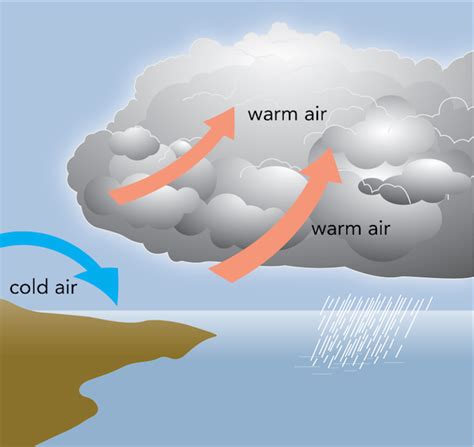
Humidity also affects air movement. Air can hold more moisture when it's warm than when it's cold. When warm air rises, it cools, and its ability to hold moisture decreases, resulting in the formation of clouds and precipitation. Cold air, on the other hand, has a lower capacity to hold moisture, making it more likely to sink.
Reason 4: Pressure
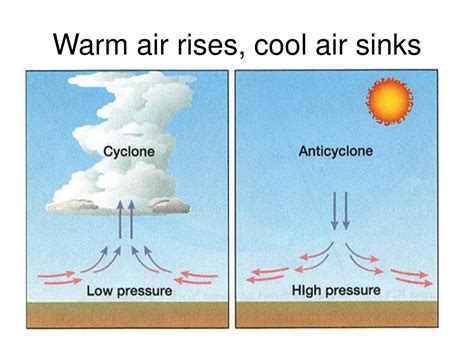
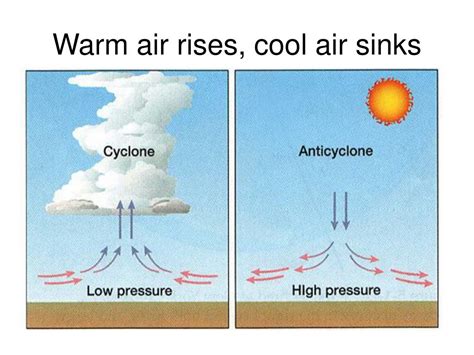
Pressure is another crucial factor in air movement. When air is heated, it expands and rises, creating an area of low pressure near the ground. This low-pressure area pulls in more air to replace the rising air. Cold air, being denser, tends to sink towards the ground, creating an area of high pressure. This high-pressure area pushes air away from the ground, causing it to spread out and sink.
Reason 5: Gravity
Lastly, gravity plays a significant role in air movement. Gravity pulls everything towards the center of the Earth, including air molecules. When air is heated, it expands and becomes less dense, allowing it to rise against the force of gravity. Cold air, being denser, is more affected by gravity and tends to sink towards the ground.
Real-World Applications of Cold Air Sinking
Understanding why cold air sinks is essential in various real-world applications, including:
- Weather forecasting: Accurate weather forecasting relies heavily on understanding air movement patterns. By knowing why cold air sinks, meteorologists can better predict weather patterns and issue timely warnings for severe weather events.
- Aviation: Pilots need to understand air movement patterns to navigate safely through the skies. Knowing why cold air sinks can help pilots avoid turbulence and other hazards.
- Architecture: Architects can design buildings that take advantage of natural air movement patterns. By understanding why cold air sinks, architects can design buildings that are more energy-efficient and comfortable to inhabit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cold air sinks due to a combination of factors, including density, temperature, humidity, pressure, and gravity. Understanding these factors is crucial in various real-world applications, from weather forecasting to architecture. By grasping the concepts outlined in this article, you'll have a better appreciation for the complex interactions that shape our atmosphere.
Cold Air Sinking Image Gallery

What causes cold air to sink?
+Cold air sinks due to a combination of factors, including density, temperature, humidity, pressure, and gravity.
Why is it essential to understand why cold air sinks?
+Understanding why cold air sinks is crucial in various real-world applications, including weather forecasting, aviation, and architecture.
How does cold air sinking affect weather patterns?
+Cold air sinking can lead to the formation of high-pressure systems, which can bring clear skies and fair weather. However, it can also lead to the formation of low-pressure systems, which can bring clouds and precipitation.
Can cold air sinking be affected by human activities?
+Yes, human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution can affect cold air sinking patterns.
How can I learn more about cold air sinking?
+You can learn more about cold air sinking by reading books and articles on meteorology, watching documentaries, and taking online courses.
