Intro
Explore the fascinating world of electromagnetic acceleration in this in-depth comparison of Gauss Rifles and Railguns. Discover the 5 key differences between these two cutting-edge technologies, including design, functionality, and applications. Learn how Gauss Rifles and Railguns harness electromagnetic forces to propel projectiles at incredible velocities, and which one holds the future of high-tech warfare.
The fascinating world of advanced electromagnetic propulsion systems has sparked intense debate and curiosity among scientists, engineers, and science fiction enthusiasts. Two technologies that have garnered significant attention are Gauss Rifles and Railguns. While both systems utilize electromagnetic forces to accelerate projectiles, they differ significantly in their underlying principles, design, and applications. In this article, we will delve into the 5 key differences between Gauss Rifles and Railguns, exploring their distinct characteristics, advantages, and potential uses.
What are Gauss Rifles and Railguns?
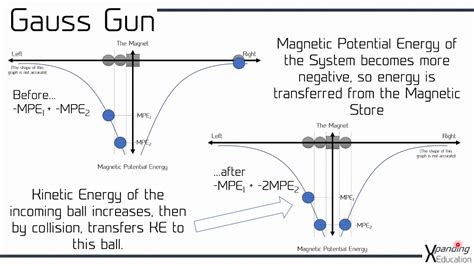
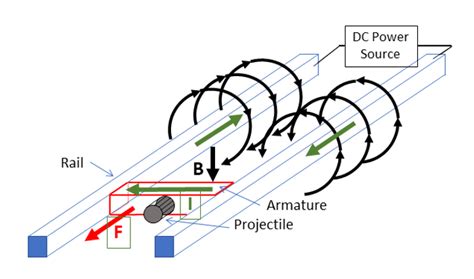
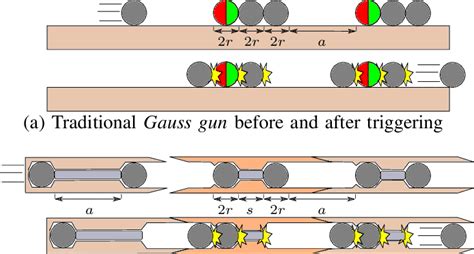
Before we dive into the differences, let's briefly introduce both technologies. Gauss Rifles, also known as Coilguns, are a type of electromagnetic propulsion system that uses a series of coils to accelerate a projectile. Each coil is energized in a sequential manner, creating a magnetic field that propels the projectile forward. Railguns, on the other hand, use a pair of parallel rails to generate a electromagnetic force that accelerates a projectile. The rails are connected to a high-voltage power source, which creates a magnetic field that propels the projectile along the rails.
Difference 1: Propulsion Mechanism
Propulsion Mechanism
The most fundamental difference between Gauss Rifles and Railguns lies in their propulsion mechanisms. Gauss Rifles use a coil-based system, where each coil is energized in sequence to create a magnetic field that propels the projectile. In contrast, Railguns rely on the Lorentz force generated by the interaction between the high-voltage power source and the rails. This difference in propulsion mechanisms affects the overall design, efficiency, and performance of both systems.
Difference 2: Energy Storage and Release
Energy Storage and Release

Gauss Rifles typically use a capacitor-based energy storage system, where energy is stored and released rapidly to energize each coil in sequence. Railguns, on the other hand, rely on a high-voltage power source, such as a capacitor bank or a generator, to create the electromagnetic force. The energy storage and release mechanisms differ significantly between the two systems, affecting their overall efficiency, reliability, and scalability.
Difference 3: Projectile Acceleration and Velocity
Projectile Acceleration and Velocity
Gauss Rifles and Railguns differ significantly in terms of projectile acceleration and velocity. Gauss Rifles typically achieve lower accelerations and velocities compared to Railguns, due to the limitations of coil-based propulsion. Railguns, on the other hand, can achieve extremely high accelerations and velocities, often exceeding several kilometers per second.
Difference 4: Design Complexity and Scalability
Design Complexity and Scalability
Gauss Rifles and Railguns exhibit distinct differences in design complexity and scalability. Gauss Rifles are generally simpler in design, with fewer components and a more straightforward architecture. Railguns, on the other hand, require a more complex design, with a higher number of components and a more intricate architecture. This difference in design complexity affects the scalability and reliability of both systems.
Difference 5: Applications and Potential Uses
Applications and Potential Uses

The final key difference between Gauss Rifles and Railguns lies in their potential applications and uses. Gauss Rifles are often proposed for use in small-scale applications, such as hobbyist projects or educational demonstrations. Railguns, on the other hand, have been explored for use in larger-scale applications, such as military systems, space exploration, and industrial processes.
Gauss Rifle Vs Railgun Image Gallery
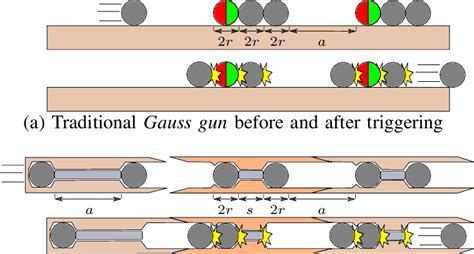





What is the main difference between Gauss Rifles and Railguns?
+The main difference between Gauss Rifles and Railguns lies in their propulsion mechanisms. Gauss Rifles use a coil-based system, while Railguns rely on the Lorentz force generated by the interaction between the high-voltage power source and the rails.
Which system is more efficient?
+Railguns are generally more efficient than Gauss Rifles, due to the higher accelerations and velocities achieved by the Lorentz force.
What are the potential applications of Gauss Rifles and Railguns?
+Gauss Rifles are often proposed for use in small-scale applications, such as hobbyist projects or educational demonstrations. Railguns, on the other hand, have been explored for use in larger-scale applications, such as military systems, space exploration, and industrial processes.
In conclusion, the differences between Gauss Rifles and Railguns are significant, ranging from their propulsion mechanisms to their potential applications. While both systems have their advantages and disadvantages, understanding these differences is crucial for developing and improving these technologies. Whether you're a scientist, engineer, or simply a curious enthusiast, exploring the world of electromagnetic propulsion systems can be a fascinating and rewarding experience.
