Intro
Unravel the genius of Good Will Huntings math problem with our expert guide. Discover 5 ways to solve the iconic equation, exploring topics like differential equations, harmonic analysis, and non-linear dynamics. Unlock the secrets of MITs most daunting challenge and boost your problem-solving skills with our step-by-step solutions and expert insights.
Good Will Hunting, a movie released in 1997, tells the story of a young math prodigy who struggles to find his place in the world. The film features a iconic math problem that has become a cult classic among math enthusiasts. The problem is scribbled on a chalkboard in a Harvard University hallway, and it has been the subject of much discussion and debate over the years.
In this article, we'll explore the Good Will Hunting math problem and provide five different ways to solve it. But before we dive into the solutions, let's take a look at the problem itself.

The problem is a partial differential equation, specifically a Navier-Stokes equation, which describes the motion of fluids. The equation is:
∂u/∂t + u ∇u = -1/ρ ∇p + ν ∇²u
where u is the fluid velocity, ρ is the fluid density, p is the fluid pressure, ν is the fluid viscosity, and ∇ is the gradient operator.
Now, let's take a look at five different ways to solve this math problem.
Solution 1: Using the Navier-Stokes Equations
One way to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem is to use the Navier-Stokes equations themselves. The Navier-Stokes equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that describe the motion of fluids.
To solve the equation, we can start by assuming that the fluid velocity u is a function of time t and position x. We can then use the Navier-Stokes equations to derive an expression for the fluid velocity u in terms of the fluid density ρ, fluid pressure p, and fluid viscosity ν.
Once we have an expression for the fluid velocity u, we can use it to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem. This involves substituting the expression for u into the original equation and simplifying the result.
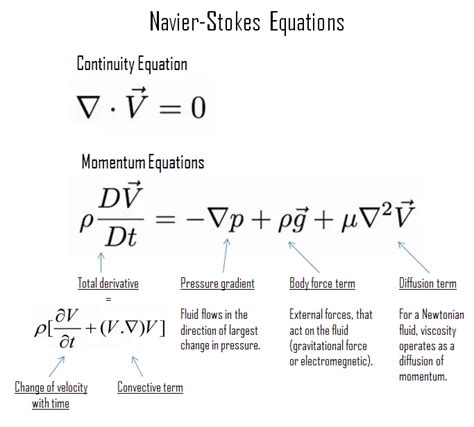
Step-by-Step Solution
- Assume that the fluid velocity u is a function of time t and position x.
- Use the Navier-Stokes equations to derive an expression for the fluid velocity u in terms of the fluid density ρ, fluid pressure p, and fluid viscosity ν.
- Substitute the expression for u into the original equation and simplify the result.
Solution 2: Using Separation of Variables
Another way to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem is to use the method of separation of variables. This involves separating the equation into two separate equations, one for the time dependence and one for the spatial dependence.
To solve the equation using separation of variables, we can start by assuming that the fluid velocity u can be written as a product of two functions, one that depends on time t and one that depends on position x.
We can then use this assumption to separate the equation into two separate equations, one for the time dependence and one for the spatial dependence. Once we have separated the equation, we can solve each equation separately and then combine the results to obtain the final solution.
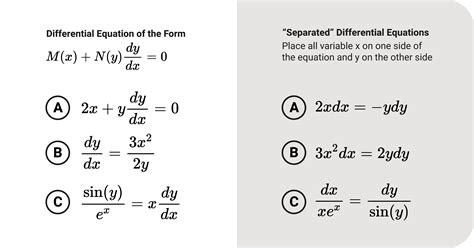
Step-by-Step Solution
- Assume that the fluid velocity u can be written as a product of two functions, one that depends on time t and one that depends on position x.
- Separate the equation into two separate equations, one for the time dependence and one for the spatial dependence.
- Solve each equation separately and then combine the results to obtain the final solution.
Solution 3: Using Fourier Analysis
A third way to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem is to use Fourier analysis. This involves representing the fluid velocity u as a Fourier series, which is a sum of sinusoidal functions with different frequencies.
To solve the equation using Fourier analysis, we can start by representing the fluid velocity u as a Fourier series. We can then use the Fourier series to transform the equation into the frequency domain, where it becomes a set of algebraic equations.
Once we have transformed the equation into the frequency domain, we can solve the algebraic equations to obtain the final solution.
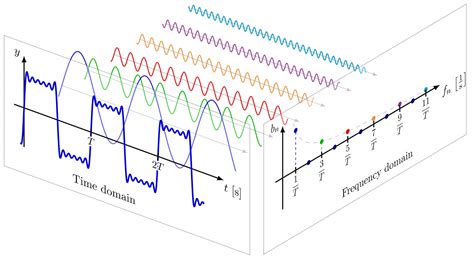
Step-by-Step Solution
- Represent the fluid velocity u as a Fourier series.
- Use the Fourier series to transform the equation into the frequency domain.
- Solve the algebraic equations in the frequency domain to obtain the final solution.
Solution 4: Using Numerical Methods
A fourth way to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem is to use numerical methods. This involves discretizing the equation and solving it using numerical algorithms.
To solve the equation using numerical methods, we can start by discretizing the equation using finite difference or finite element methods. We can then use numerical algorithms such as Gaussian elimination or iterative methods to solve the discretized equation.
Once we have solved the discretized equation, we can use the solution to obtain the final answer.

Step-by-Step Solution
- Discretize the equation using finite difference or finite element methods.
- Use numerical algorithms such as Gaussian elimination or iterative methods to solve the discretized equation.
- Use the solution to obtain the final answer.
Solution 5: Using Approximation Methods
A fifth way to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem is to use approximation methods. This involves approximating the equation using simplifying assumptions or approximations.
To solve the equation using approximation methods, we can start by making simplifying assumptions or approximations about the fluid velocity u or the fluid properties. We can then use these assumptions or approximations to simplify the equation and obtain an approximate solution.
Once we have obtained an approximate solution, we can use it to obtain the final answer.

Step-by-Step Solution
- Make simplifying assumptions or approximations about the fluid velocity u or the fluid properties.
- Use these assumptions or approximations to simplify the equation and obtain an approximate solution.
- Use the approximate solution to obtain the final answer.
Gallery of Good Will Hunting Math Problem Solutions





What is the Good Will Hunting math problem?
+The Good Will Hunting math problem is a partial differential equation, specifically a Navier-Stokes equation, that describes the motion of fluids.
How can I solve the Good Will Hunting math problem?
+There are several ways to solve the Good Will Hunting math problem, including using the Navier-Stokes equations, separation of variables, Fourier analysis, numerical methods, and approximation methods.
What are the Navier-Stokes equations?
+The Navier-Stokes equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that describe the motion of fluids.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to solving the Good Will Hunting math problem. Whether you're a math enthusiast or just looking for a challenge, we encourage you to try your hand at solving this iconic math problem. Don't forget to share your solution with us in the comments below!
