Intro
Improve your French listening skills with Heard In French, a valuable resource for mastering the language. Discover how to effectively use this tool to boost comprehension, vocabulary, and pronunciation. Learn to navigate various accents, expressions, and nuances, and take your French to the next level with expert explanations and insider tips.
The French language is renowned for its melodic sound and intricate grammar. For many learners, one of the most significant challenges is grasping the nuances of French pronunciation, particularly when it comes to the various accents and diacritical marks that can completely alter the meaning of a word. Heard in French is a crucial aspect of mastering the language, as it allows speakers to convey subtle shades of meaning and express themselves with precision.
The Importance of Mastering Heard in French
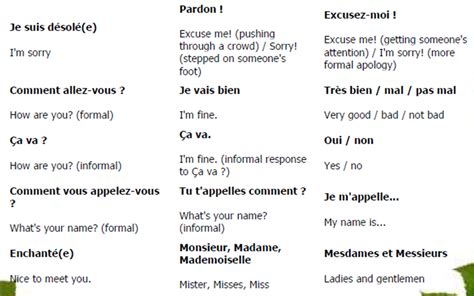
French is a language that relies heavily on the use of accents and diacritical marks to distinguish between words that are otherwise identical. For example, the word "à" (with a grave accent) means "to" or "at," while the word "a" (without an accent) is a indefinite article. Similarly, the word "é" (with an acute accent) means "he" or "it," while the word "e" (without an accent) is a preposition. Mastering heard in French is essential to convey the correct meaning and avoid confusion.
Understanding the Different Accents in French
French has five different accents: the acute accent (é), the grave accent (à), the circumflex accent (ô), the diaeresis (ü), and the cedilla (ç). Each accent has a specific pronunciation and is used to distinguish between words that are otherwise identical.
- The acute accent (é) is pronounced with a slight rising intonation, indicating that the word has a different meaning than its unaccented counterpart.
- The grave accent (à) is pronounced with a slight falling intonation, indicating that the word has a different meaning than its unaccented counterpart.
- The circumflex accent (ô) is pronounced with a slight rising and then falling intonation, indicating that the word has a different meaning than its unaccented counterpart.
- The diaeresis (ü) is pronounced with a slight separation between the two vowels, indicating that the word has a different meaning than its unaccented counterpart.
- The cedilla (ç) is pronounced with a soft "c" sound, indicating that the word has a different meaning than its unaccented counterpart.

The Benefits of Mastering Heard in French
Mastering heard in French has numerous benefits for language learners. It allows speakers to convey subtle shades of meaning and express themselves with precision, which is essential for effective communication. Additionally, mastering heard in French can help learners to:
- Improve their pronunciation and intonation
- Enhance their vocabulary and comprehension
- Develop a more nuanced understanding of the language
- Communicate more effectively with native speakers
Tips for Mastering Heard in French
Mastering heard in French requires practice and dedication, but with the right tips and strategies, learners can improve their skills and become proficient in the language. Here are some tips for mastering heard in French:
- Listen to native speakers and pay attention to their pronunciation and intonation
- Practice speaking and listening to improve your pronunciation and comprehension
- Use language learning apps and resources to practice hearing and repeating French words
- Read French texts and practice reading aloud to improve your pronunciation and intonation
- Focus on the most common accents and diacritical marks in French, such as the acute and grave accents
Common Challenges When Mastering Heard in French
While mastering heard in French can be a rewarding experience, it also comes with its challenges. Here are some common challenges that learners may face:
- Difficulty in distinguishing between similar-sounding words
- Trouble with pronunciation and intonation
- Limited vocabulary and comprehension
- Difficulty in understanding native speakers
Overcoming Challenges in Mastering Heard in French
While challenges are inevitable, there are ways to overcome them and achieve mastery in heard in French. Here are some strategies for overcoming common challenges:
- Practice regularly and consistently to improve your pronunciation and comprehension
- Focus on building your vocabulary and comprehension
- Use language learning apps and resources to practice hearing and repeating French words
- Listen to native speakers and pay attention to their pronunciation and intonation
- Seek feedback from language instructors or native speakers to improve your skills
Mastering Heard in French: Real-Life Applications
Mastering heard in French has numerous real-life applications, from communicating with native speakers to reading and writing in French. Here are some examples of how mastering heard in French can be applied in real-life situations:
- Communicating with native speakers: Mastering heard in French allows speakers to communicate effectively with native speakers, which is essential for building relationships and achieving success in personal and professional settings.
- Reading and writing in French: Mastering heard in French is essential for reading and writing in French, which is a crucial skill for anyone who wants to work or study in a French-speaking country.
- Enhancing career opportunities: Mastering heard in French can enhance career opportunities, particularly in fields such as international business, diplomacy, and education.

Conclusion
Mastering heard in French is a crucial aspect of mastering the French language, and it requires practice, dedication, and the right strategies. By understanding the different accents and diacritical marks in French, learners can improve their pronunciation and comprehension, and develop a more nuanced understanding of the language. With its numerous benefits and real-life applications, mastering heard in French is an essential skill for anyone who wants to communicate effectively in French.
Mastering Heard in French Image Gallery








What is the importance of mastering heard in French?
+Mastering heard in French is essential for communicating effectively in French, as it allows speakers to convey subtle shades of meaning and express themselves with precision.
What are the different accents in French?
+French has five different accents: the acute accent (é), the grave accent (à), the circumflex accent (ô), the diaeresis (ü), and the cedilla (ç).
How can I improve my French pronunciation?
+Practice speaking and listening to improve your pronunciation, use language learning apps and resources to practice hearing and repeating French words, and focus on building your vocabulary and comprehension.
