Intro
Discover the importance of comprehensive sex education in high school, covering topics like consent, relationships, and reproductive health, to promote informed decisions and healthy lifestyles among teenagers.
The importance of sex education in high schools cannot be overstated. As adolescents navigate the complexities of puberty and young adulthood, they require comprehensive guidance on reproductive health, relationships, and safety. Sex education is a critical component of a well-rounded education, enabling students to make informed decisions about their bodies, well-being, and futures. Despite its significance, sex education remains a contentious issue in many countries, with debates surrounding its implementation, content, and effectiveness. In this article, we will delve into the world of sex education in high schools, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices.
The need for sex education in high schools is evident in the alarming rates of teenage pregnancy, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and sexual violence. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 11% of all births worldwide are to girls under the age of 20. Furthermore, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that nearly 20% of high school students in the United States have had sex before the age of 15. These statistics underscore the urgent need for comprehensive sex education that addresses the physical, emotional, and social aspects of human relationships.
Benefits of Sex Education

Key Components of Sex Education
A comprehensive sex education program should include the following key components: * Human anatomy and physiology * Puberty and adolescent development * Reproductive health and hygiene * Relationships and communication * Consent and boundaries * STIs and HIV prevention * Contraception and family planning * Sexual orientation and gender identity * Media literacy and critical thinkingChallenges and Controversies

Addressing Challenges and Controversies
To address these challenges and controversies, educators, policymakers, and community leaders must work together to develop and implement comprehensive sex education programs that are evidence-based, inclusive, and respectful of diverse perspectives. This can involve: * Collaborating with parents, teachers, and community members to develop curriculum standards and guidelines * Providing teacher training and support to ensure effective implementation * Allocating sufficient funding and resources to support sex education programs * Engaging with diverse stakeholders to address cultural and religious sensitivities * Incorporating LGBTQ+ perspectives and experiences into sex education curriculaBest Practices in Sex Education

Evaluating Sex Education Programs
To evaluate the effectiveness of sex education programs, educators and policymakers should use a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures, including: * Student surveys and feedback * Pre- and post-test assessments * Longitudinal studies and follow-up evaluations * Parent and teacher evaluations * Community engagement and participation metricsGallery of Sex Education Images
Sex Education Image Gallery

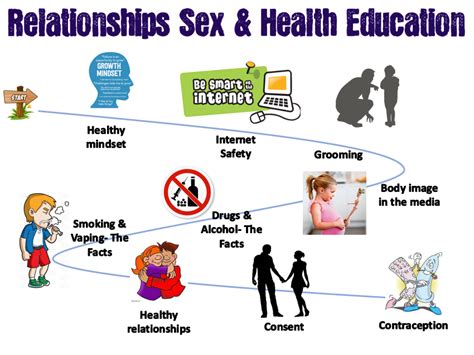






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of sex education in high schools?
+The purpose of sex education in high schools is to provide students with comprehensive and accurate information about reproductive health, relationships, and safety, enabling them to make informed decisions about their bodies and well-being.
What are the key components of a comprehensive sex education program?
+A comprehensive sex education program should include human anatomy and physiology, puberty and adolescent development, reproductive health and hygiene, relationships and communication, consent and boundaries, STIs and HIV prevention, contraception and family planning, and sexual orientation and gender identity.
How can sex education programs be evaluated and improved?
+Sex education programs can be evaluated and improved through a combination of quantitative and qualitative measures, including student surveys and feedback, pre- and post-test assessments, longitudinal studies and follow-up evaluations, parent and teacher evaluations, and community engagement and participation metrics.
What are some common challenges and controversies surrounding sex education?
+Some common challenges and controversies surrounding sex education include abstinence-only vs. comprehensive sex education, parental consent and involvement, teacher training and support, curriculum development and standards, funding and resource allocation, cultural and religious sensitivities, and LGBTQ+ inclusion and representation.
How can educators and policymakers address these challenges and controversies?
+Educators and policymakers can address these challenges and controversies by collaborating with parents, teachers, and community members to develop curriculum standards and guidelines, providing teacher training and support, allocating sufficient funding and resources, engaging with diverse stakeholders to address cultural and religious sensitivities, and incorporating LGBTQ+ perspectives and experiences into sex education curricula.
As we conclude our exploration of sex education in high schools, we invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and perspectives on this critical topic. How can we work together to ensure that all students receive comprehensive and inclusive sex education, empowering them to make informed decisions about their bodies, relationships, and futures? Join the conversation by commenting below, sharing this article with your networks, or engaging with us on social media. Together, we can create a more informed, compassionate, and supportive community that prioritizes the health, well-being, and empowerment of all individuals.
