Intro
Discover the inner workings of an infantry platoon and squad, the backbone of modern military tactical units. Learn about the structure, roles, and responsibilities of these units, including team and fireteam composition, leadership, and communication. Understand the key elements that enable effective infantry operations, from reconnaissance to combat maneuvers.
The infantry platoon and squad are the fundamental building blocks of a military organization, serving as the basic tactical units on the battlefield. Understanding the structure and dynamics of these units is essential for effective military operations.
Infantry Platoon Structure
An infantry platoon typically consists of 20-50 soldiers, led by a platoon leader (usually a lieutenant or second lieutenant) and assisted by a platoon sergeant. The platoon is further divided into two or more squads, each led by a squad leader. The platoon's structure is designed to facilitate command and control, allowing the platoon leader to coordinate and execute missions effectively.
Key Positions within an Infantry Platoon
- Platoon Leader: Responsible for commanding the platoon and making tactical decisions.
- Platoon Sergeant: Assists the platoon leader, oversees platoon operations, and coordinates logistics.
- Squad Leaders: Lead squads, execute missions, and provide feedback to the platoon leader.
- Team Leaders: Lead teams within squads, execute tasks, and report to squad leaders.
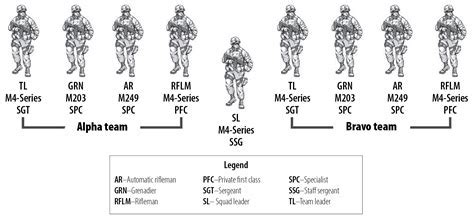
Infantry Squad Structure
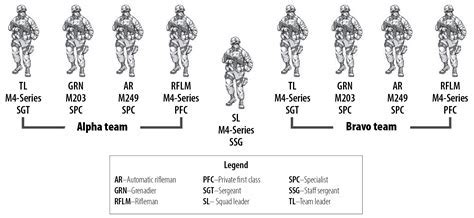
An infantry squad typically consists of 9-12 soldiers, led by a squad leader. The squad is further divided into two or more teams, each led by a team leader. The squad's structure is designed to facilitate tactical operations, allowing the squad leader to coordinate and execute tasks effectively.
Key Positions within an Infantry Squad
- Squad Leader: Responsible for commanding the squad, making tactical decisions, and coordinating team operations.
- Team Leaders: Lead teams, execute tasks, and report to the squad leader.
- Team Members: Execute tasks, provide security, and support team operations.
Tactical Operations

Infantry platoons and squads are designed to execute a variety of tactical operations, including:
- Patrols: Reconnaissance, security, and combat patrols.
- Raids: Surprise attacks on enemy positions or installations.
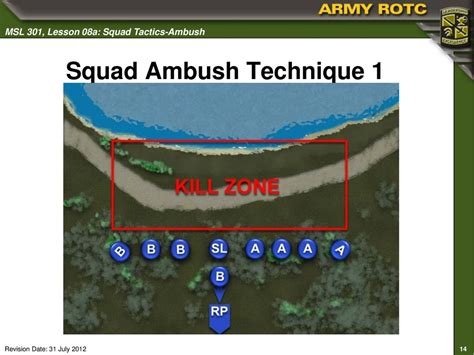
- Ambushes: Covert attacks on enemy units.
- Defensive operations: Securing and defending positions.
Tactical Considerations
- Terrain: The natural environment can significantly impact tactical operations.
- Enemy forces: Understanding the enemy's strength, disposition, and intentions is crucial.
- Logistics: Ensuring adequate supplies, transportation, and communication is essential.
- Morale: Maintaining unit cohesion and morale is critical for effective operations.
Leadership and Communication

Effective leadership and communication are essential for successful infantry platoon and squad operations.
- Leaders must clearly articulate missions, objectives, and expectations.
- Communication must be concise, clear, and timely.
- Leaders must foster a culture of trust, discipline, and accountability.
Key Leadership Principles
- Lead by example: Demonstrate the behavior and values expected of subordinates.
- Provide clear guidance: Ensure subordinates understand the mission, objectives, and expectations.
- Foster teamwork: Encourage collaboration, mutual support, and collective success.
Training and Preparation

Infantry platoons and squads must undergo rigorous training and preparation to ensure effectiveness.
- Training must focus on developing individual and collective skills.
- Platoons and squads must rehearse and practice tactics, techniques, and procedures.
- Leaders must emphasize the importance of safety, security, and risk management.
Key Training Principles
- Train as you fight: Replicate real-world scenarios and conditions.
- Focus on the fundamentals: Develop individual and collective skills.
- Practice, practice, practice: Rehearse and refine tactics, techniques, and procedures.
Gallery of Infantry Platoon and Squad Operations
Infantry Platoon and Squad Operations





What is the typical structure of an infantry platoon?
+An infantry platoon typically consists of 20-50 soldiers, led by a platoon leader and assisted by a platoon sergeant. The platoon is further divided into two or more squads, each led by a squad leader.
What is the role of a squad leader in an infantry squad?
+A squad leader is responsible for commanding the squad, making tactical decisions, and coordinating team operations.
What are some key leadership principles for infantry platoon and squad leaders?
+Key leadership principles include leading by example, providing clear guidance, and fostering teamwork.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the structure and dynamics of infantry platoons and squads. By understanding the roles, responsibilities, and key principles of these units, military leaders can optimize their effectiveness and achieve success on the battlefield.
