Intro
Explore James Madison calendar events, featuring historical reenactments, founding father seminars, and patriotic celebrations, honoring Americas fourth president and his legacy in US history and politics.
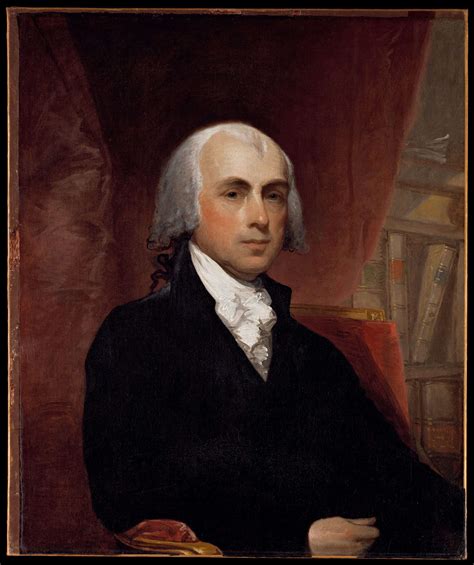
The life and legacy of James Madison, the fourth President of the United States, are a testament to his enduring impact on American history. As the principal author of the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights, Madison's contributions to the country's foundation are immeasurable. His presidency, which spanned from 1809 to 1817, was marked by significant events that shaped the nation's future. In this article, we will delve into the key calendar events of James Madison's life, exploring his early years, presidency, and later life.
Madison's early life was marked by a strong educational foundation, which would later serve him well in his political career. Born on March 16, 1751, in Port Conway, Virginia, Madison was the oldest of twelve children. His family's modest means and strong values instilled in him a sense of responsibility and a commitment to public service. As we explore Madison's life, it becomes clear that his experiences and relationships played a significant role in shaping his political ideology and informing his decisions as President.
The significance of Madison's life and legacy cannot be overstated. His contributions to American history are a testament to his vision, leadership, and commitment to the principles of democracy. As we examine the key calendar events of his life, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical context in which he lived and the challenges he faced as President. From the War of 1812 to the establishment of the Second Bank of the United States, Madison's presidency was marked by significant events that continue to shape American politics and society today.
Early Life and Education

Rise to Prominence

Presidency

Key Events of the Presidency
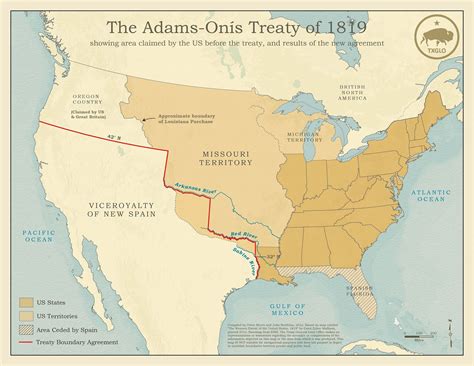
Some of the key events of Madison's presidency include: * The War of 1812: This conflict was fought between the United States and the British Empire, and it would ultimately lead to the signing of the Treaty of Ghent, which ended the war. * The establishment of the Second Bank of the United States: This institution was established in 1816, and it would play a crucial role in stabilizing the nation's economy. * The Tariff of 1816: This legislation was passed in 1816, and it would provide protection for American industries and help to promote economic growth. * The acquisition of Florida: In 1819, Madison negotiated the Adams-Onis Treaty, which led to the acquisition of Florida from Spain.Later Life and Legacy

Assessment of Madison's Legacy
Madison's legacy can be assessed in several ways: * His contributions to the United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights: Madison's work on these documents helped to establish the foundation of American democracy. * His leadership during the War of 1812: Madison's leadership during this conflict helped to shape the nation's response to the war and to negotiate a favorable peace treaty. * His commitment to the principles of democracy: Madison's commitment to democracy and individual liberties helped to shape the nation's political culture and to promote the growth of American democracy.James Madison Image Gallery









What were James Madison's major accomplishments as President?
+James Madison's major accomplishments as President include leading the country through the War of 1812, establishing the Second Bank of the United States, and negotiating the Adams-Onis Treaty, which led to the acquisition of Florida from Spain.
What was James Madison's role in the development of the United States Constitution?
+James Madison played a key role in the development of the United States Constitution, serving as the principal author of the document and helping to establish the framework of the federal government.
What was James Madison's legacy?
+James Madison's legacy is complex and multifaceted, reflecting both the accomplishments and challenges of his presidency. He is remembered for his commitment to the principles of democracy and his vision for a strong and unified nation.
As we reflect on the life and legacy of James Madison, it is clear that his contributions to American history are immeasurable. From his early years to his presidency and later life, Madison's commitment to the principles of democracy and his vision for a strong and unified nation continue to inspire Americans today. We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative look at the key calendar events of James Madison's life, and we invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this important topic. Whether you are a historian, a student, or simply someone interested in learning more about American history, we encourage you to explore the life and legacy of James Madison and to consider the ways in which his contributions continue to shape our nation today.
