Intro
Discover the Messerschmitt Bf 110, a formidable German heavy fighter aircraft that dominated the skies of World War II as a deadly night fighter, equipped with advanced radar technology and heavy armament, playing a crucial role in the Luftwaffes defense against Allied bombers, night intruders, and reconnaissance planes.
The Messerschmitt Bf 110, also known as the Me 110, was a heavy fighter aircraft used by the German Luftwaffe during World War II. Designed by Willy Messerschmitt, the Bf 110 was initially intended as a long-range escort fighter, but it eventually became one of the deadliest night fighters of the war.
The Development of the Bf 110

The Bf 110 was first conceived in 1934, when the German Ministry of Aviation (Reichsluftfahrtministerium) issued a requirement for a long-range escort fighter. Messerschmitt's design, which would eventually become the Bf 110, was selected from among several competing proposals. The aircraft made its first flight in May 1936 and entered production in 1938.
Design and Features
The Bf 110 was a twin-engine aircraft, powered by two Daimler-Benz DB 601 engines. It had a crew of two, consisting of a pilot and a radio operator/gunner. The aircraft was heavily armed, with two 20mm MG FF cannons and four 7.92mm MG 17 machine guns. The Bf 110 also had a range of over 1,000 miles, making it well-suited for long-range escort missions.
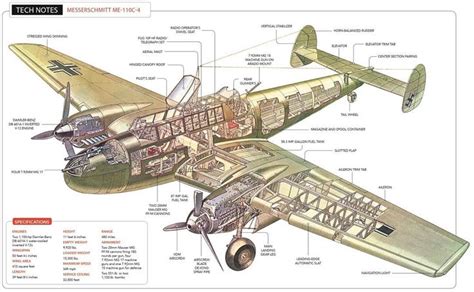
The Bf 110 as a Night Fighter
Despite its initial design as an escort fighter, the Bf 110 ultimately found its true calling as a night fighter. The aircraft's combination of heavy armament, long range, and advanced radar systems made it an ideal platform for intercepting and destroying enemy bombers at night.

The Bf 110's night fighting career began in 1940, when the Luftwaffe formed its first night fighter unit, NJG 1. Equipped with the Bf 110, NJG 1 began intercepting and destroying British bombers on nighttime raids over Germany. The Bf 110's success as a night fighter led to the development of specialized night fighter variants, including the Bf 110G-4 and the Bf 110G-4/R3.
Radar and Interception Techniques
The Bf 110's night fighting success was largely due to its advanced radar systems. The aircraft was equipped with the FuG 202 Lichtenstein BC radar system, which allowed the pilot to detect and track enemy aircraft at night. The Bf 110's radar system was so effective that it became the standard for German night fighters throughout the war.
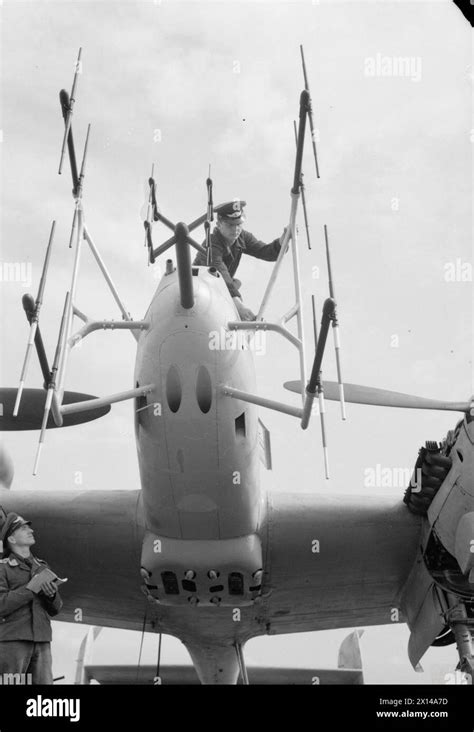

The Bf 110's night fighting tactics typically involved a combination of radar-guided interception and visual identification. The pilot would use the radar system to locate and track the enemy aircraft, and then use visual identification to confirm the target and attack.
Operational History
The Bf 110 saw extensive service throughout World War II, operating on the Eastern and Western fronts. The aircraft was used in a variety of roles, including night fighting, day fighting, and ground attack.

The Bf 110's night fighting career was particularly notable, with the aircraft accounting for thousands of Allied bomber kills. The Bf 110's success as a night fighter earned it a reputation as one of the deadliest aircraft of the war.
Notable Aces
Several notable German aces flew the Bf 110 during the war. One of the most famous was Major Heinz-Wolfgang Schnaufer, who scored 121 night fighter kills in the Bf 110.

Legacy
The Messerschmitt Bf 110 played a significant role in the history of aerial warfare. Its combination of heavy armament, long range, and advanced radar systems made it an ideal platform for night fighting, and its success in this role earned it a reputation as one of the deadliest aircraft of World War II.

The Bf 110's legacy extends beyond its military service, however. The aircraft's design influenced the development of post-war fighter aircraft, and its advanced radar systems paved the way for modern air defense systems.
Preserved Aircraft
Several Messerschmitt Bf 110s have been preserved and are on display in museums around the world. One notable example is the Bf 110G-4 on display at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C.

Gallery of Messerschmitt Bf 110 Images
Messerschmitt Bf 110 Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What was the primary role of the Messerschmitt Bf 110?
+The primary role of the Messerschmitt Bf 110 was as a heavy fighter and night fighter.
What was the Bf 110's top speed?
+The Bf 110's top speed was approximately 380 mph.
How many Bf 110s were produced during World War II?
+Approximately 6,170 Bf 110s were produced during World War II.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the Messerschmitt Bf 110, one of the deadliest night fighters of World War II. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about this fascinating aircraft, please don't hesitate to comment below.
