Intro
Delve into the psychological enigma of nightmares and uncover the underlying causes of these disturbing nocturnal experiences. Explore the connection between nightmares, mental health, and the subconscious mind, and discover how to overcome the anxiety and fear they evoke, revealing a path towards a more peaceful and restful sleep.
The concept of nightmares has long fascinated and unsettled humans. These disturbing episodes of sleep, characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and terror, can leave a lasting impact on our waking lives. Despite their prevalence, nightmares remain shrouded in mystery, with many questions surrounding their causes, effects, and significance. In this article, we will delve into the psychological realm of nightmares, exploring their underlying mechanisms, triggers, and potential meanings.
Understanding Nightmares
Nightmares are a universal human experience, affecting approximately 80% of adults worldwide. These distressing episodes typically occur during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, when brain activity is heightened and dreams are most vivid. Nightmares can manifest in various forms, ranging from fleeting, disconnected images to complex, narrative-driven scenarios. Despite their diversity, nightmares share a common thread – the presence of intense negative emotions, such as fear, anxiety, and sadness.
Theories Behind Nightmares
Researchers have proposed several theories to explain the occurrence of nightmares. One prominent hypothesis suggests that nightmares are an adaptive response to stress, allowing the brain to process and consolidate emotional experiences in a safe environment. This theory is supported by the finding that nightmares often reflect unresolved conflicts, unexpressed emotions, and unconscious fears.
Another theory posits that nightmares are a result of the brain's attempt to regulate emotions, particularly those related to fear and anxiety. During REM sleep, the brain's emotional centers are active, and the lack of inhibitory control allows for the unchecked expression of negative emotions, leading to the manifestation of nightmares.
Triggers and Contributing Factors
While the exact causes of nightmares are still unknown, several triggers and contributing factors have been identified:
- Stress and anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can increase the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
- Sleep disorders: Sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to an increased risk of nightmares.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as sedatives and antidepressants, can alter sleep patterns and increase the likelihood of nightmares.
- Sleep stage: Nightmares typically occur during the REM stage of sleep, when brain activity is heightened and dreams are most vivid.
- Genetics: Research suggests that nightmares may have a genetic component, with certain individuals being more prone to experiencing nightmares due to their genetic makeup.

Psychological Implications of Nightmares
Nightmares can have a significant impact on an individual's mental health and well-being. Repeated exposure to nightmares can lead to:
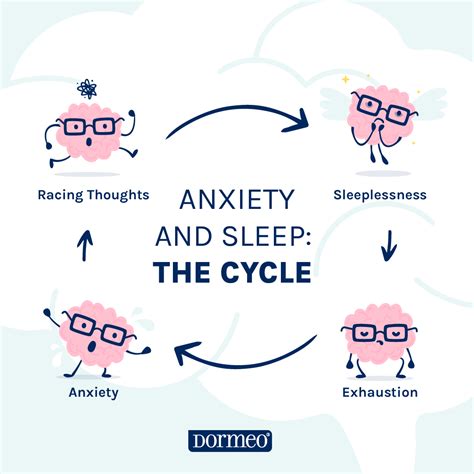
- Anxiety and stress: The distressing nature of nightmares can contribute to increased anxiety and stress levels, affecting daily functioning and overall quality of life.
- Sleep disturbances: Nightmares can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, daytime fatigue, and other sleep-related problems.
- Mood regulation: The negative emotions associated with nightmares can affect mood regulation, contributing to the development of depression and other mood disorders.
- Trauma and PTSD: Nightmares can be a symptom of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a condition characterized by the re-experiencing of traumatic events.
Coping with Nightmares
While nightmares can be distressing, there are several strategies that can help alleviate their impact:
- Keeping a dream journal: Recording dreams and nightmares can help identify recurring themes and triggers.
- Relaxation techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualization, can reduce stress and anxiety levels.
- Imagery rehearsal therapy: This technique involves re-imagining the nightmare scenario in a more positive or empowering way, reducing the distressing impact of the nightmare.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: This form of therapy can help individuals address underlying issues and develop coping strategies to manage nightmares.
Gallery of Nightmare-Related Images
Nightmare Image Gallery









FAQs
What are nightmares?
+Nightmares are distressing episodes of sleep characterized by intense fear, anxiety, and terror.
What causes nightmares?
+Nightmares can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, anxiety, sleep disorders, medications, and genetics.
How can I cope with nightmares?
+Strategies for coping with nightmares include keeping a dream journal, practicing relaxation techniques, imagery rehearsal therapy, and cognitive-behavioral therapy.
In conclusion, nightmares are a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, influenced by a variety of psychological, emotional, and environmental factors. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and triggers of nightmares, individuals can take steps to alleviate their impact and improve overall sleep quality and mental health.
