Intro
Discover the intricacies of Operation Deny Flight, NATOs pivotal 1990s air campaign in the Balkans. Learn how this extensive operation enforced no-fly zones, conducted airstrikes, and implemented sanctions to curb Bosnian War atrocities. Explore the military strategies, international politics, and humanitarian efforts that defined this complex conflict, shaped by the United Nations, EU, and US involvement.
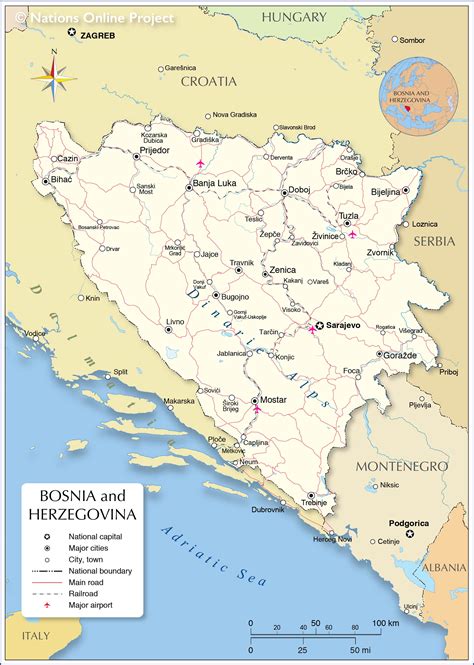
The 1990s were a tumultuous time for the Balkans, marked by intense conflict and humanitarian crises. In response to the escalating violence, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) launched Operation Deny Flight, a significant air campaign aimed at enforcing a no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina. This operation marked a pivotal moment in NATO's history, as it demonstrated the alliance's willingness to intervene in regional conflicts and protect civilians from harm.

Operation Deny Flight was initiated on April 12, 1993, in response to the worsening situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The conflict, which began in 1992, had resulted in widespread human suffering, displacement, and violence. The United Nations (UN) had previously imposed a no-fly zone over the region, but it lacked the necessary enforcement mechanisms. NATO's intervention aimed to fill this gap and prevent further escalation of the conflict.
Key Objectives and Strategies
Operation Deny Flight had several key objectives:
- Enforce the no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Protect civilians from harm
- Support UN peacekeeping efforts
- Deter belligerent parties from using airpower
To achieve these objectives, NATO employed a range of strategies, including:
- Aerial surveillance and monitoring
- Interception of unauthorized flights
- Enforcement of the no-fly zone through military action
- Coordination with UN peacekeeping forces
Airpower and Military Assets
Operation Deny Flight involved a significant array of airpower and military assets. NATO deployed a range of aircraft, including fighter jets, transport planes, and helicopters. These assets were drawn from various NATO member countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany.

Command Structure and Cooperation
Operation Deny Flight was conducted under the command of NATO's Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR). The operation involved close cooperation between NATO and UN forces, as well as with other international organizations.
- NATO-UN Cooperation: NATO worked closely with the UN to ensure that its air campaign supported the broader peacekeeping efforts. This cooperation involved regular coordination and communication between NATO and UN commanders.
- International Partnerships: Operation Deny Flight also involved partnerships with other international organizations, such as the European Community (EC) and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE).
Impact and Legacy
Operation Deny Flight had a significant impact on the conflict in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The air campaign helped to:
- Enforce the No-Fly Zone: NATO's enforcement of the no-fly zone prevented belligerent parties from using airpower, which reduced the risk of civilian casualties and helped to stabilize the situation.
- Protect Civilians: The operation helped to protect civilians from harm, particularly in urban areas where they were most vulnerable.
- Support UN Peacekeeping: Operation Deny Flight supported UN peacekeeping efforts, which helped to create a more secure environment for humanitarian aid delivery and other peacebuilding activities.
Lessons Learned and Future Implications
Operation Deny Flight provided valuable lessons for future NATO operations. These lessons include:
- Importance of Cooperation: The operation highlighted the importance of cooperation between NATO and other international organizations, such as the UN.
- Role of Airpower: Operation Deny Flight demonstrated the effectiveness of airpower in enforcing no-fly zones and protecting civilians.
- Need for Flexibility: The operation showed that military operations must be flexible and adaptable to respond to changing circumstances on the ground.
Challenges and Controversies
Operation Deny Flight was not without its challenges and controversies. Some of the key issues included:
- Rules of Engagement: The operation's rules of engagement were criticized for being too restrictive, which limited the ability of NATO aircraft to engage hostile targets.
- Civilians Casualties: Despite efforts to minimize civilian casualties, some incidents occurred, which sparked controversy and criticism.
- Cooperation with UN: While NATO-UN cooperation was generally effective, some issues arose, particularly with regard to command and control arrangements.
Operation Deny Flight Image Gallery





What was the main objective of Operation Deny Flight?
+The main objective of Operation Deny Flight was to enforce a no-fly zone over Bosnia and Herzegovina and protect civilians from harm.
Which countries participated in Operation Deny Flight?
+Operation Deny Flight involved a range of countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and Germany.
What were some of the challenges faced by Operation Deny Flight?
+Some of the challenges faced by Operation Deny Flight included restrictive rules of engagement, civilian casualties, and cooperation with UN forces.
As we reflect on Operation Deny Flight, it is clear that the operation had a significant impact on the conflict in Bosnia and Herzegovina. The lessons learned from this operation continue to inform NATO's approach to crisis management and conflict resolution.
