Intro
Discover how the Panzerfaust, a German anti-tank rocket, revolutionized Africas WWII battlefield. Learn how its innovative design and tactics impacted the North African Campaign, influencing the wars outcome. Explore the 5 key ways the Panzerfaust shaped Africas WWII landscape, from empowering infantry to counter-balancing Allied armor superiority.
The Panzerfaust, a German anti-tank rocket-propelled grenade, played a significant role in shaping Africa's World War II battlefield. While often overshadowed by other theaters of operation, the North African Campaign saw intense fighting between Axis and Allied forces. The Panzerfaust's impact on this campaign was substantial, and here are five ways it shaped the battlefield:

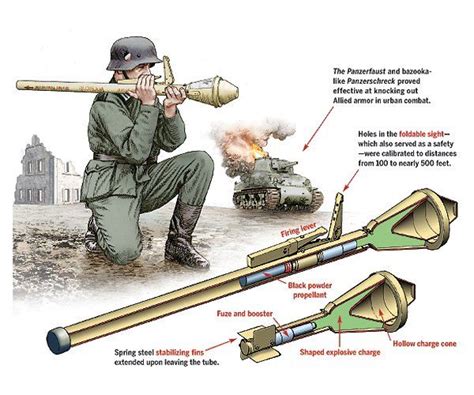
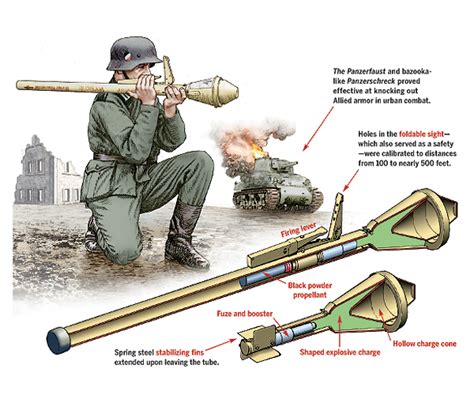
The Panzerfaust's introduction in 1943 provided German forces with a much-needed boost in their anti-tank capabilities. This handheld, single-shot weapon was effective against Allied armor, which had been gaining the upper hand in North Africa. The Panzerfaust's ability to penetrate armor and disable tanks gave German troops a newfound confidence on the battlefield.
Increased Mobility and Flexibility
The Panzerfaust's portability and ease of use allowed German troops to employ it in a variety of situations, from urban warfare to desert combat. Its compact size and lightweight design enabled soldiers to carry the Panzerfaust into tight spaces, making it an ideal weapon for ambushes and flanking maneuvers. This increased mobility and flexibility gave German forces an edge in adapting to the ever-changing North African battlefield.
Enhanced Anti-Tank Capabilities
The Panzerfaust's effectiveness against armor was a significant concern for Allied forces. Its 60mm warhead could penetrate up to 200mm of armor, making it a formidable opponent for Allied tanks. German troops used the Panzerfaust to devastating effect, taking out enemy tanks and disrupting supply lines. The Panzerfaust's anti-tank capabilities forced Allied commanders to reassess their tactics and develop new strategies to counter the German advantage.
Impact on Allied Tank Design
The Panzerfaust's success on the battlefield prompted Allied forces to reevaluate their tank designs. The Allies began to develop thicker armor and more sophisticated tank designs to counter the Panzerfaust's threat. This led to the creation of tanks like the M26 Pershing, which featured thicker armor and improved firepower. The Panzerfaust's impact on tank design can still be seen in modern tanks, which prioritize armor and mobility to counter anti-tank threats.
Tactical Innovations and Adaptations
The Panzerfaust's effectiveness led to the development of new tactics and adaptations by both German and Allied forces. German troops began to employ the Panzerfaust in conjunction with other anti-tank weapons, creating complex ambushes and defensive positions. Allied forces responded by developing countermeasures, such as the use of infantry screens and tank escorts, to mitigate the Panzerfaust's impact. This cat-and-mouse game drove innovation and adaptation on both sides, shaping the battlefield in profound ways.

In conclusion, the Panzerfaust played a significant role in shaping Africa's World War II battlefield. Its impact on mobility, anti-tank capabilities, tank design, and tactical innovations and adaptations cannot be overstated. As a testament to its enduring legacy, the Panzerfaust remains an important part of military history, serving as a reminder of the constantly evolving nature of warfare.
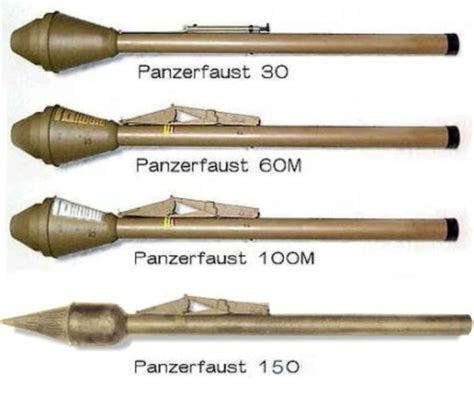
Gallery of Panzerfaust Images
Panzerfaust Image Gallery








FAQs
What was the Panzerfaust's main advantage on the battlefield?
+The Panzerfaust's main advantage was its ability to penetrate armor and disable tanks, making it a formidable opponent for Allied forces.
How did the Panzerfaust impact tank design?
+The Panzerfaust's success prompted Allied forces to develop thicker armor and more sophisticated tank designs, such as the M26 Pershing.
What were some of the tactical innovations and adaptations that arose from the Panzerfaust's use?
+The Panzerfaust's use led to the development of new tactics, such as the use of infantry screens and tank escorts, and the employment of complex ambushes and defensive positions.
