Intro
Boost decision-making efficiency by avoiding nonstarters. Learn how to identify and eliminate unviable options, streamlining your process with effective critical thinking, cognitive biases awareness, and structured decision-making techniques. Discover the pitfalls of nonstarters and make informed choices with our expert insights on decision analysis, risk assessment, and optimization strategies.
Decision making is a critical aspect of personal and professional life. Every day, individuals and organizations make numerous decisions that impact their lives, businesses, and communities. However, the decision-making process is not always straightforward, and there are common pitfalls that can lead to suboptimal choices. One of the most significant obstacles to effective decision making is the nonstarter. In this article, we will explore the concept of nonstarters, their impact on decision making, and strategies for avoiding them.
Understanding Nonstarters

Nonstarters are options, ideas, or alternatives that are so clearly unsuitable or unworkable that they should be eliminated from consideration at the outset. Nonstarters can be tempting, especially when they seem attractive or innovative. However, they often lead to wasted time, resources, and effort. Nonstarters can arise from various sources, including:
- Lack of information or understanding
- Unrealistic expectations or assumptions
- Biased or flawed thinking
- Insufficient analysis or evaluation
The Impact of Nonstarters on Decision Making
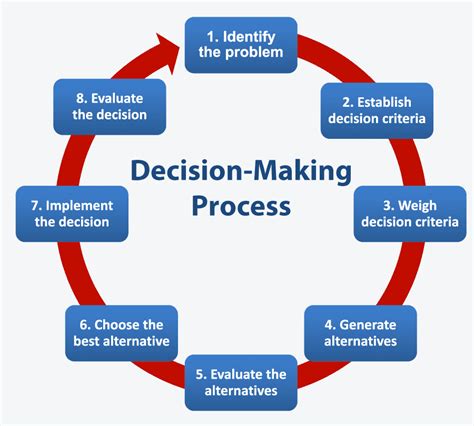
Nonstarters can significantly hinder the decision-making process, leading to:
- Inefficient use of time and resources
- Delayed or suboptimal decisions
- Increased risk and uncertainty
- Decreased confidence and trust in the decision-making process
- Missed opportunities and lost value
Strategies for Avoiding Nonstarters
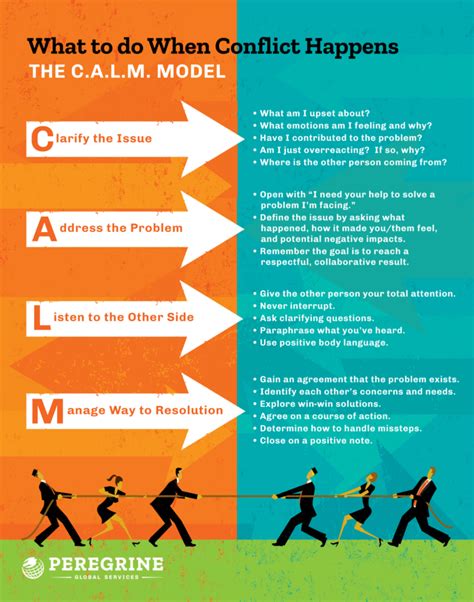
To avoid nonstarters, consider the following strategies:
- Define clear objectives and criteria: Establish clear goals, objectives, and criteria for the decision-making process. This will help to eliminate nonstarters and focus on viable options.
- Gather relevant information: Collect and analyze relevant data, facts, and insights to inform the decision-making process.
- Evaluate options systematically: Use a systematic approach to evaluate options, considering factors such as feasibility, cost, risk, and potential impact.
- Encourage diverse perspectives: Seek input from diverse stakeholders and experts to identify potential nonstarters and alternative solutions.
- Avoid biases and assumptions: Recognize and challenge biases and assumptions that may lead to nonstarters.
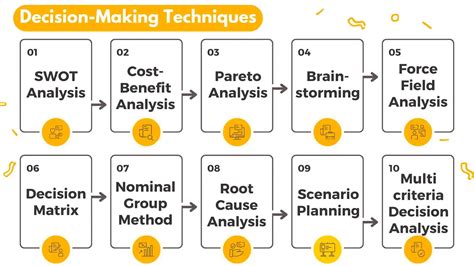
- Use decision-making frameworks and tools: Utilize decision-making frameworks and tools, such as decision trees, Pareto analysis, or SWOT analysis, to structure the decision-making process and avoid nonstarters.
- Develop a culture of critical thinking: Foster a culture of critical thinking and constructive criticism to identify and eliminate nonstarters.
Best Practices for Effective Decision Making
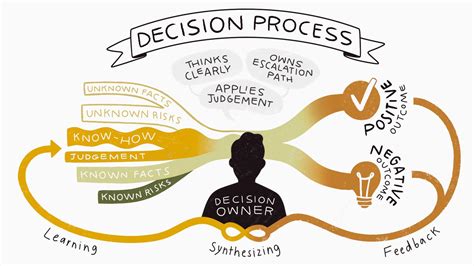
To ensure effective decision making, consider the following best practices:
- Involve diverse stakeholders: Engage diverse stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the issue and potential solutions.
- Use data-driven insights: Leverage data-driven insights to inform the decision-making process and avoid relying on intuition or anecdotal evidence.
- Encourage transparency and accountability: Foster a culture of transparency and accountability to ensure that decision-making processes are clear, fair, and justifiable.
- Develop a decision-making framework: Establish a decision-making framework that outlines the key steps, stakeholders, and criteria for decision making.
- Monitor and evaluate decisions: Regularly monitor and evaluate decisions to ensure that they are effective and achieve the desired outcomes.
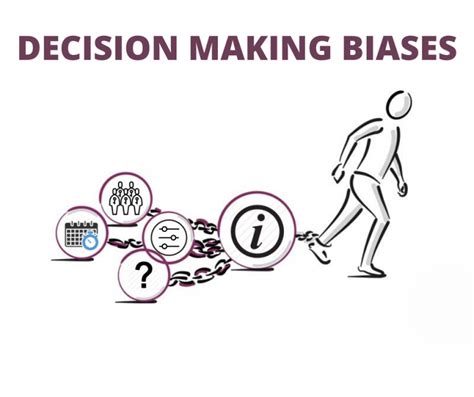
Common Pitfalls in Decision Making

Common pitfalls in decision making include:
- Confirmation bias: The tendency to seek information that confirms existing biases or assumptions.
- Anchoring bias: The tendency to rely too heavily on the first piece of information encountered when making a decision.
- Availability heuristic: The tendency to overestimate the importance or likelihood of information that is readily available.
- Hindsight bias: The tendency to believe, after an event has occurred, that it was predictable and that one would have predicted it.
Gallery of Decision Making Strategies
Decision Making Strategies Image Gallery




What are nonstarters in decision making?
+Nonstarters are options, ideas, or alternatives that are so clearly unsuitable or unworkable that they should be eliminated from consideration at the outset.
How can I avoid nonstarters in decision making?
+To avoid nonstarters, define clear objectives and criteria, gather relevant information, evaluate options systematically, and encourage diverse perspectives.
What are common pitfalls in decision making?
+Common pitfalls in decision making include confirmation bias, anchoring bias, availability heuristic, and hindsight bias.
In conclusion, avoiding nonstarters is essential for effective decision making. By understanding the concept of nonstarters, their impact on decision making, and strategies for avoiding them, individuals and organizations can make better decisions and achieve their goals. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and practical advice for improving decision-making processes. If you have any further questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
