Intro
Discover the crucial distinction between reliability and accuracy. Understand how reliability ensures consistency, while accuracy guarantees correctness. Learn the implications of these concepts in various fields, including science, research, and everyday decision-making. Get clarity on the nuances of reliable vs accurate data, methods, and results to make informed choices.
In everyday life, we often use the terms "reliable" and "accurate" interchangeably, assuming they mean the same thing. However, in various fields such as science, engineering, and quality control, the distinction between these two terms is crucial. Understanding the difference between reliable and accurate can help us make informed decisions, evaluate information, and improve our overall judgment.
Imagine you're trying to get to work on time, and you have two options: a bus that leaves exactly at 8:00 AM every day, but takes a longer route, and a train that usually leaves around 8:00 AM, but takes a shorter route. Which one would you choose? If you prioritize punctuality, you might prefer the bus, but if you value speed, the train might be a better option. In this scenario, the bus is reliable, but not necessarily accurate, while the train is accurate, but not always reliable.

In this article, we'll delve into the differences between reliability and accuracy, explore their significance in various contexts, and provide examples to illustrate their meanings.
What is Reliability?
Reliability refers to the consistency or dependability of a process, system, or measurement. It describes the ability of something to produce consistent results over time, under various conditions, and with minimal errors. In other words, reliability measures how well something performs its intended function, without necessarily considering its accuracy.
For instance, a reliable weather forecast might predict rain every day, but the actual amount of rainfall might vary significantly. In this case, the forecast is reliable, but not necessarily accurate.
Types of Reliability
There are several types of reliability, including:
- Inter-rater reliability: The degree of agreement between two or more observers or raters.
- Test-retest reliability: The consistency of results when a test or measurement is repeated over time.
- Parallel forms reliability: The consistency of results between two or more versions of a test or measurement.
What is Accuracy?
Accuracy, on the other hand, refers to the closeness of a measurement or result to its true value. It describes the degree to which something is correct, precise, or free from error. In other words, accuracy measures how well something conforms to reality.
Using the weather forecast example again, an accurate forecast would predict the exact amount of rainfall, temperature, and other conditions. In this case, the forecast is accurate, but not necessarily reliable.
Types of Accuracy
There are several types of accuracy, including:
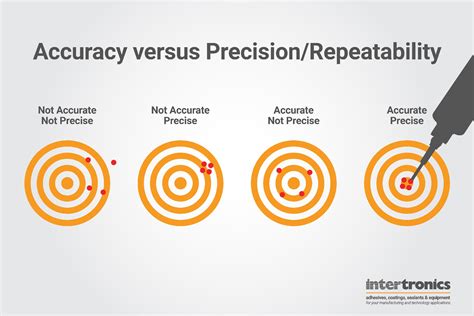
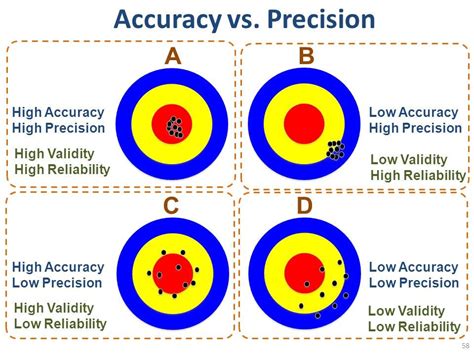
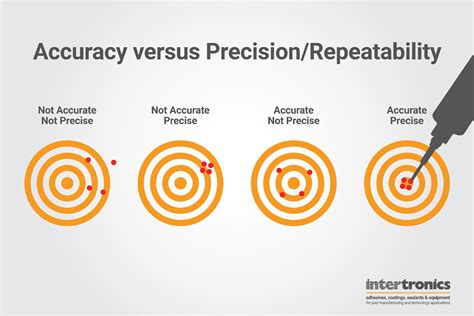
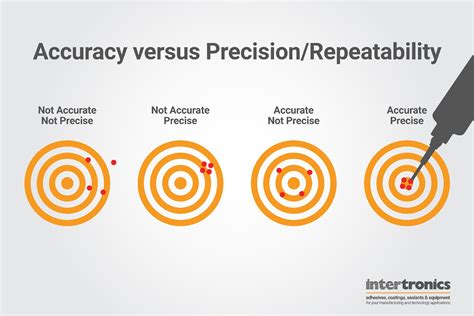
- Precision: The degree of closeness of repeated measurements to each other.
- Validity: The degree to which a measurement or result reflects the true value or concept being measured.
- Calibration: The process of adjusting a measurement or instrument to ensure its accuracy.

Key Differences Between Reliability and Accuracy
While reliability and accuracy are related concepts, they are distinct and serve different purposes. Here are some key differences:
- Reliability focuses on consistency, while accuracy focuses on correctness.
- Reliability measures the degree of agreement or consistency, while accuracy measures the degree of closeness to the true value.
- Reliability is concerned with the process or system, while accuracy is concerned with the outcome or result.
Real-World Examples
To illustrate the differences between reliability and accuracy, consider the following examples:
- A manufacturing process that produces parts with consistent dimensions is reliable, but if the dimensions are not accurate, the parts may not fit together correctly.
- A medical test that consistently produces the same results is reliable, but if the results are not accurate, the diagnosis may be incorrect.
- A GPS navigation system that consistently provides directions is reliable, but if the directions are not accurate, you may get lost.
Why is the Distinction Important?
Understanding the difference between reliability and accuracy is crucial in various fields, including:
- Quality control: Ensuring that products or services meet specifications and are free from defects.
- Research: Validating results and ensuring that data is accurate and reliable.
- Decision-making: Making informed decisions based on reliable and accurate information.
Practical Applications
The distinction between reliability and accuracy has practical applications in various areas, including:
- Engineering: Designing systems and processes that are both reliable and accurate.
- Healthcare: Developing medical tests and treatments that are both reliable and accurate.
- Finance: Making investment decisions based on reliable and accurate financial data.
Gallery of Reliable and Accurate Images
Reliable vs Accurate Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between reliability and accuracy?
+Reliability refers to the consistency or dependability of a process, system, or measurement, while accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement or result to its true value.
Why is it important to distinguish between reliability and accuracy?
+Understanding the difference between reliability and accuracy is crucial in various fields, including quality control, research, and decision-making, as it helps ensure that products, services, and results meet specifications and are free from defects.
Can something be reliable but not accurate?
+Yes, something can be reliable but not accurate. For example, a manufacturing process that produces parts with consistent dimensions is reliable, but if the dimensions are not accurate, the parts may not fit together correctly.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between reliability and accuracy is essential in various contexts. While reliability focuses on consistency and dependability, accuracy focuses on correctness and precision. By recognizing the distinction between these two concepts, we can make informed decisions, improve our judgment, and ensure that products, services, and results meet specifications and are free from defects.
