Intro
Unlock the secrets of a perfect paint job with our expert guide on Palette Prime. Discover 7 game-changing ways to achieve flawless finishes, from surface preparation to primer selection. Master the art of Palette Prime and elevate your painting skills with our in-depth tutorial, covering primer application, paint adhesion, and color consistency.
The world of art and design has long been fascinated by the concept of color and its impact on human perception. At the heart of this fascination lies the often-misunderstood realm of color theory, where the subtle nuances of hue, saturation, and contrast come together to create a visual language that speaks to us on a deep, emotional level. One of the most fundamental yet mysterious aspects of color theory is the notion of a "palette prime" - a seemingly elusive concept that has left many artists, designers, and enthusiasts scratching their heads in search of answers.
So, what exactly is a palette prime, and how can we unlock its secrets to create truly stunning works of art? In this article, we'll delve into the world of color theory and explore seven ways to crack the riddle of palette prime.
Understanding the Basics of Color Theory
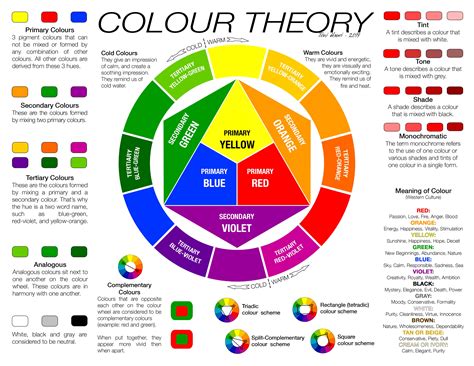
Before we can begin to understand the concept of palette prime, we need to lay the groundwork with a solid grasp of color theory fundamentals. Color theory is the study of how colors interact with each other and with the human eye. It's a vast and complex subject that encompasses everything from the color wheel to the intricacies of color harmony and contrast.
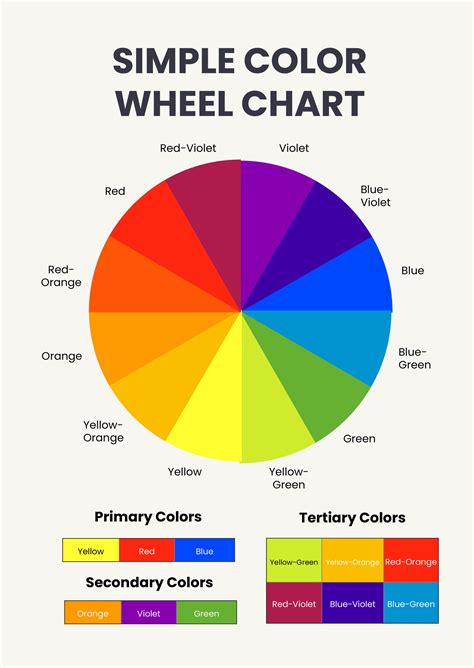
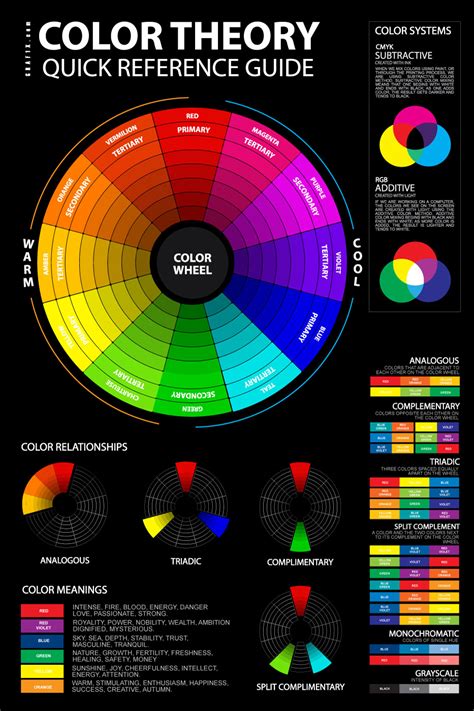
At its core, color theory is based on the idea that colors can be grouped into primary, secondary, and tertiary categories. Primary colors (red, yellow, and blue) are the base colors that can't be created by mixing other colors together. Secondary colors (orange, green, and purple) are created by mixing two primary colors, while tertiary colors are created by mixing primary and secondary colors.
Color Harmony and Contrast
Color harmony and contrast are two of the most critical aspects of color theory. Color harmony refers to the way colors work together to create a visually appealing effect, while contrast refers to the way colors interact with each other to create a sense of tension or visual interest.
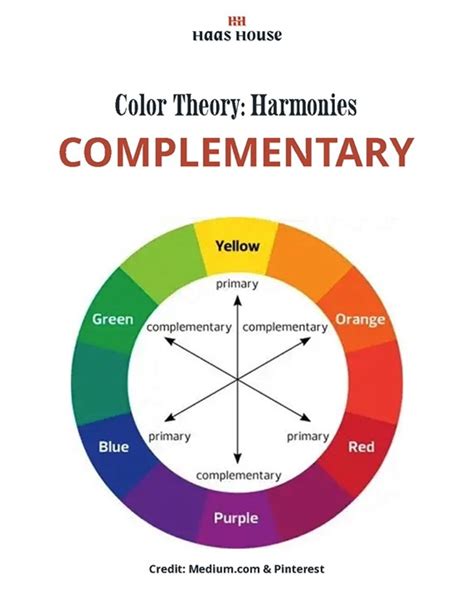
There are several principles of color harmony, including complementary, analogous, and triadic color schemes. Complementary color schemes involve pairing colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, while analogous color schemes involve pairing colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. Triadic color schemes involve pairing colors that are equally spaced from each other on the color wheel.
Unpacking the Mystery of Palette Prime

So, what exactly is a palette prime, and how does it fit into the world of color theory? A palette prime is a set of colors that are specifically chosen to work together in harmony, creating a visual language that is both aesthetically pleasing and emotionally resonant.
In essence, a palette prime is a carefully curated selection of colors that are designed to evoke a particular mood, atmosphere, or emotional response. It's a delicate balancing act that requires a deep understanding of color theory, as well as a keen eye for nuance and subtlety.
Seven Ways to Crack the Riddle of Palette Prime
So, how can we unlock the secrets of palette prime and create truly stunning works of art? Here are seven ways to crack the riddle:
- Start with a clear concept or theme: Before you can begin to build a palette prime, you need to have a clear idea of what you're trying to achieve. What's the theme or concept of your artwork? What emotions do you want to evoke? What's the mood or atmosphere you're trying to create?
- Choose a dominant color: A dominant color is the color that sets the tone for the entire palette. It's the color that will anchor the rest of the palette and provide a sense of continuity and cohesion.
- Select complementary colors: Complementary colors are colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel. They create a sense of contrast and visual interest, and can be used to add depth and dimension to your artwork.
- Experiment with analogous colors: Analogous colors are colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. They create a sense of harmony and continuity, and can be used to add nuance and subtlety to your artwork.
- Consider the 60-30-10 rule: The 60-30-10 rule is a simple guideline for building a palette prime. It suggests that 60% of the palette should be a dominant color, 30% a secondary color, and 10% an accent color.
- Don't forget about neutrals: Neutrals are colors that are not part of the dominant color scheme, but can be used to add contrast and visual interest. They can also be used to create a sense of balance and harmony.
- Trust your instincts: Finally, don't be afraid to trust your instincts. Building a palette prime is all about experimentation and exploration. Don't be afraid to try new things and take risks.
Putting it all Together
So, how do we put all of these principles into action? Let's take a look at an example of a palette prime in action.
Imagine you're creating a painting of a sunset over a peaceful lake. You want to evoke a sense of calm and serenity, and create a visual language that is both soothing and emotionally resonant.
You start by choosing a dominant color - in this case, a warm orange-yellow color that captures the essence of the sunset. You then select complementary colors - blues and greens that are opposite the dominant color on the color wheel. You experiment with analogous colors - warm yellows and oranges that are next to the dominant color on the color wheel.
You consider the 60-30-10 rule, using the dominant color for 60% of the palette, a secondary color for 30%, and an accent color for 10%. You add neutrals to create contrast and visual interest, and trust your instincts to guide the process.
The result is a palette prime that is both aesthetically pleasing and emotionally resonant - a visual language that speaks to us on a deep, emotional level.
Gallery of Color Theory
Color Theory Image Gallery






FAQs
What is a palette prime?
+A palette prime is a set of colors that are specifically chosen to work together in harmony, creating a visual language that is both aesthetically pleasing and emotionally resonant.
How do I create a palette prime?
+To create a palette prime, start by choosing a dominant color, then select complementary colors, experiment with analogous colors, and consider the 60-30-10 rule. Don't forget to add neutrals to create contrast and visual interest.
What is the 60-30-10 rule?
+The 60-30-10 rule is a simple guideline for building a palette prime. It suggests that 60% of the palette should be a dominant color, 30% a secondary color, and 10% an accent color.
We hope this article has helped you crack the riddle of palette prime and unlock the secrets of color theory. Remember, building a palette prime is all about experimentation and exploration - don't be afraid to try new things and trust your instincts. Happy creating!
