Intro
Explore the T Class Submarine, Britains unsung maritime hero of World War II. Discover its history, design, and operations, as well as its role in Allied victories. Learn about its robust build, advanced armament, and stealth capabilities, making it a formidable force against Axis powers. Dive into the story of this remarkable vessel.
In the dark days of World War II, the British Royal Navy played a pivotal role in the Allied victory. Among the numerous warships and submarines that served with distinction, the T-class submarines stand out for their remarkable service. These sleek and powerful vessels were a testament to British engineering and maritime prowess, and their exploits continue to fascinate historians and naval enthusiasts alike.
The T-class submarines were designed and built by British shipyards between 1937 and 1945, with a total of 15 boats constructed during the war years. These submarines were intended to serve as attack vessels, capable of launching torpedoes against enemy shipping and naval forces. With their streamlined hulls, powerful diesel-electric propulsion systems, and formidable armament, the T-class submarines were among the most advanced underwater warships of their time.
Design and Construction
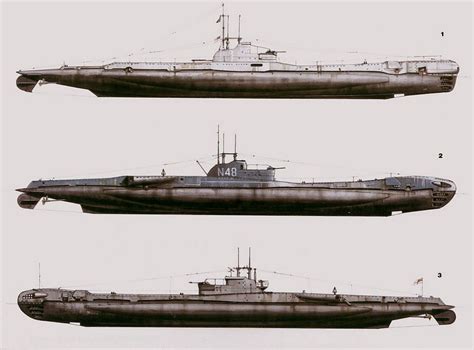
The T-class submarines were designed by the British Admiralty's Naval Construction Department, with the first boat, HMS Thunderbolt, being laid down in 1937. The design was influenced by the earlier S-class submarines, but with significant improvements in terms of size, speed, and armament. The T-class boats were 275 feet (84 meters) long, with a beam of 27 feet (8.2 meters) and a draft of 13 feet (4 meters). They displaced around 1,300 tons of water when submerged and had a top speed of 15.5 knots (28.7 km/h) on the surface.
Main Armament
The T-class submarines were heavily armed with a combination of torpedoes, guns, and mines. Their main armament consisted of six 21-inch (533mm) torpedo tubes, with a total of 12 torpedoes carried on board. The boats also had a single 4-inch (102mm) gun mounted on the conning tower, which was used for surface attacks and defending against enemy aircraft.
Operational History
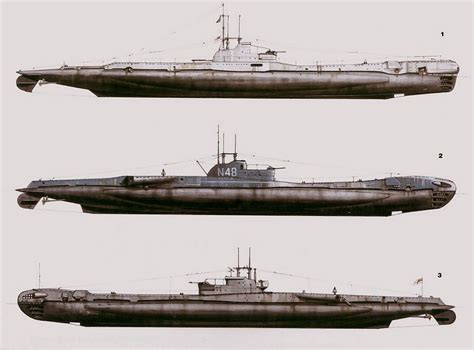
The T-class submarines saw extensive service during World War II, operating in various theaters including the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Indian Oceans. These boats played a significant role in disrupting enemy shipping and naval operations, sinking numerous German and Italian warships, as well as merchant vessels.
One notable example of the T-class submarines' exploits was the sinking of the Italian battleship Conte di Cavour by HMS Thunderbolt in 1940. Another notable achievement was the sinking of the German cruiser Blücher by HMS Triad in 1940.
Tactical Innovations
The T-class submarines were also at the forefront of tactical innovations, introducing new tactics and techniques that would become standard for submarine warfare. These included the use of wolfpack tactics, where multiple submarines coordinated their attacks to overwhelm enemy defenses. The T-class boats also pioneered the use of radar and sonar systems, which greatly improved their ability to detect and track enemy targets.
Legacy

The T-class submarines played a significant role in the Allied victory in World War II, and their legacy continues to be felt today. These boats were instrumental in developing the tactics and techniques that would become standard for submarine warfare, and their design influenced the development of post-war submarines.
The T-class submarines also demonstrated the importance of submarine warfare in modern naval operations, highlighting the need for advanced underwater capabilities to counter enemy shipping and naval forces. Today, the legacy of the T-class submarines can be seen in the advanced submarines operated by navies around the world.
Preservation Efforts
Several T-class submarines have been preserved as museums or memorials, serving as a testament to their historic significance. HMS Tantalus, for example, is now a museum ship in Australia, while HMS Truant is a memorial in the United Kingdom.
T-class Submarine Image Gallery








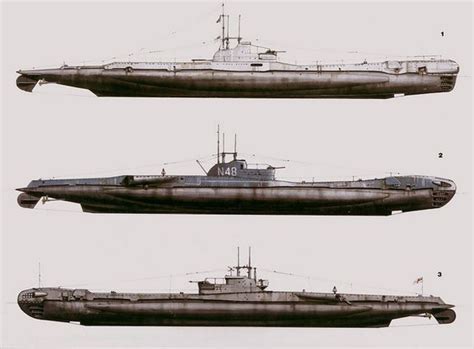
What was the main purpose of the T-class submarines?
+The T-class submarines were designed as attack vessels, intended to launch torpedoes against enemy shipping and naval forces.
How many T-class submarines were built during World War II?
+A total of 15 T-class submarines were constructed during the war years.
What was the top speed of the T-class submarines?
+The T-class submarines had a top speed of 15.5 knots (28.7 km/h) on the surface.
We hope you've enjoyed this in-depth look at the T-class submarines, one of the most iconic and influential submarine designs of World War II. These remarkable vessels played a crucial role in the Allied victory, and their legacy continues to inspire and educate people around the world.
