Intro
Unlock the full potential of TouchDesigners Optical Flow palette with our expert guide. Master 5 essential techniques to harness the power of optical flow, including motion detection, tracking, and visualization. Discover how to enhance your visuals, automate workflows, and create stunning effects with this comprehensive tutorial.
Optical flow is a fundamental concept in computer vision, and when combined with the versatility of TouchDesigner, it can lead to stunning visual effects and innovative solutions. The Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner is a powerful tool that allows you to analyze and manipulate the motion of pixels between two images or frames. In this article, we will delve into the world of optical flow and explore five ways to master the Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner.
What is Optical Flow?
Optical flow is the pattern of apparent motion of pixels between two consecutive frames in a video or image sequence. It is a 2D vector field that represents the motion of each pixel in the image. Optical flow is widely used in various fields, including computer vision, robotics, and film production, for tasks such as motion analysis, object tracking, and motion estimation.
Getting Started with the Optical Flow Palette
The Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner is a set of nodes and tools that enable you to analyze and manipulate the optical flow between two images or frames. To get started, you need to create a new TouchDesigner project and add the Optical Flow palette to your workspace. You can do this by right-clicking in the Network Editor and selecting "Palette" > "Optical Flow."
1. Basic Optical Flow Analysis
The first step in mastering the Optical Flow palette is to understand how to perform basic optical flow analysis. This involves using the Optical Flow nodes to calculate the motion of pixels between two images or frames. To do this, you need to connect the Optical Flow node to two image inputs, which can be either still images or video frames.
Calculating Optical Flow
To calculate the optical flow, you need to adjust the parameters of the Optical Flow node, such as the window size, iterations, and smoothing. The window size determines the size of the neighborhood used to calculate the optical flow, while the iterations control the number of times the algorithm is run. Smoothing helps to reduce noise in the optical flow output.
2. Visualizing Optical Flow
Visualizing the optical flow is essential to understanding the motion of pixels between two images or frames. TouchDesigner provides several ways to visualize the optical flow, including the use of vector fields, color maps, and particle simulations.
Vector Field Visualization
One common way to visualize the optical flow is to use a vector field. This can be done by connecting the Optical Flow node to a Vector Field node, which displays the motion of pixels as arrows or lines.
3. Advanced Optical Flow Techniques
Once you have mastered the basics of optical flow analysis and visualization, you can move on to more advanced techniques. These include using multiple Optical Flow nodes to analyze different regions of the image, using different algorithms to improve accuracy, and combining optical flow with other computer vision techniques.
Multi-Region Optical Flow Analysis
One advanced technique is to use multiple Optical Flow nodes to analyze different regions of the image. This can be done by connecting multiple Optical Flow nodes to different regions of the image input, using techniques such as masking or cropping.
4. Real-World Applications of Optical Flow
Optical flow has numerous real-world applications, including object tracking, motion analysis, and video editing. In TouchDesigner, you can use the Optical Flow palette to create interactive installations, motion graphics, and visual effects.
Object Tracking with Optical Flow
One common application of optical flow is object tracking. By analyzing the motion of pixels between two frames, you can track the movement of objects in a scene. This can be done by connecting the Optical Flow node to a Tracking node, which uses the optical flow output to estimate the position and velocity of objects.
5. Tips and Tricks for Mastering the Optical Flow Palette
Finally, here are some tips and tricks for mastering the Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner:
- Use the right algorithm: Choose the right optical flow algorithm for your specific use case, such as the Lucas-Kanade algorithm for sparse optical flow or the Horn-Schunck algorithm for dense optical flow.
- Adjust parameters: Adjust the parameters of the Optical Flow node, such as the window size, iterations, and smoothing, to optimize the output.
- Use multiple nodes: Use multiple Optical Flow nodes to analyze different regions of the image or to combine different algorithms.
- Visualize the output: Use visualization techniques, such as vector fields or color maps, to understand the output of the Optical Flow node.
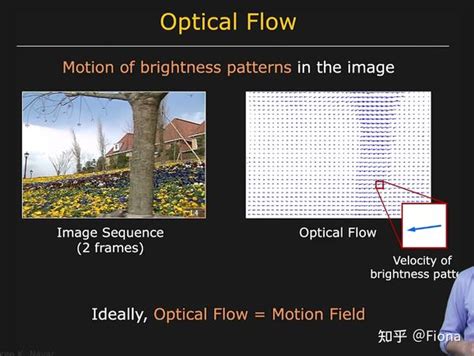
Gallery of Optical Flow Images
Optical Flow Image Gallery
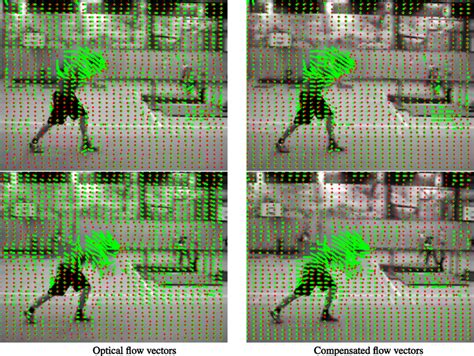
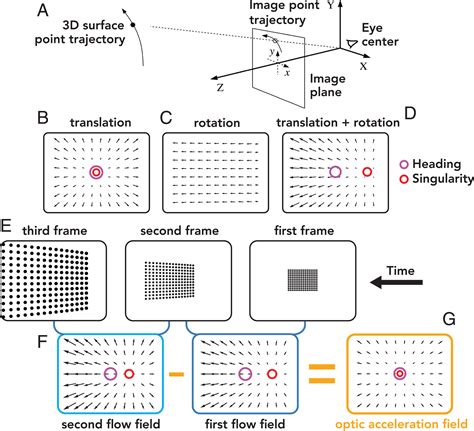

FAQs
What is optical flow?
+Optical flow is the pattern of apparent motion of pixels between two consecutive frames in a video or image sequence.
How do I use the Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner?
+To use the Optical Flow palette, create a new TouchDesigner project, add the Optical Flow palette to your workspace, and connect the Optical Flow node to two image inputs.
What are some common applications of optical flow?
+Optical flow has numerous real-world applications, including object tracking, motion analysis, and video editing.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Optical Flow palette in TouchDesigner. With practice and experimentation, you can master the techniques outlined in this article and create stunning visual effects and innovative solutions.
