Intro
Unlock the power of critical theory in todays complex world. Discover 5 key takeaways from Tysons Critical Theory Today, exploring intersectionality, social justice, and the impact of systemic inequalities. Learn how to apply critical thinking to everyday life, challenge dominant narratives, and foster inclusive communities through transformative knowledge.
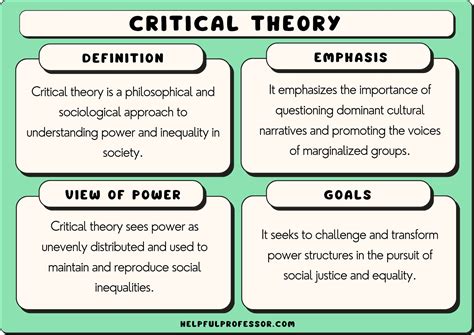
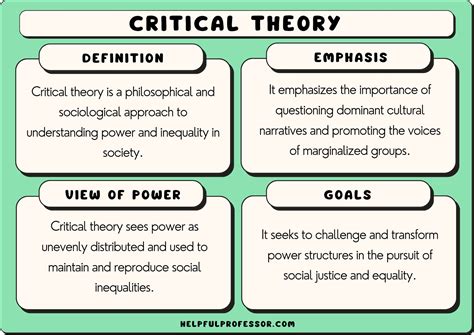
Critical theory, a philosophical approach that critiques social and political power structures, has been a crucial part of academic discourse for decades. One of the key figures in this field is Lois Tyson, whose work has had a significant impact on the development of critical theory. Here are five key takeaways from Lois Tyson's critical theory today:
1. The Importance of Contextualization
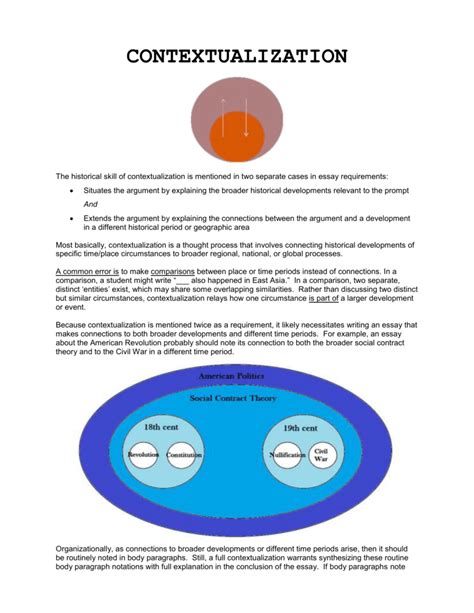
Tyson's critical theory emphasizes the importance of contextualization in understanding literary and cultural texts. She argues that texts must be analyzed within their historical, social, and cultural contexts to uncover their underlying power dynamics and ideological messages. This approach recognizes that texts are not static entities, but rather dynamic and complex artifacts that reflect and shape the world around us.
Understanding Contextualization
Contextualization involves considering the social, cultural, and historical factors that influence the creation and reception of texts. This includes examining the author's background, the cultural and historical context in which the text was written, and the social and cultural norms that shape the text's meaning. By contextualizing texts, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the power dynamics and ideological messages that underlie them.
2. The Role of Power and Ideology in Shaping Culture

Tyson's critical theory also highlights the role of power and ideology in shaping culture. She argues that cultural texts, including literature, art, and film, reflect and reinforce dominant ideologies and power structures. These texts often perpetuate oppressive ideologies, such as racism, sexism, and homophobia, by presenting them as natural or normal.
Understanding Power and Ideology
Power and ideology are closely intertwined in critical theory. Power refers to the ability to shape and control cultural narratives, while ideology refers to the underlying systems of beliefs and values that justify and maintain those narratives. By examining the power dynamics and ideological messages in cultural texts, readers can gain a deeper understanding of how culture shapes and reflects societal norms and values.
3. The Importance of Intersectionality

Tyson's critical theory emphasizes the importance of intersectionality in understanding cultural texts. Intersectionality refers to the idea that different forms of oppression, such as racism, sexism, and homophobia, intersect and overlap to create complex and nuanced systems of oppression.
Understanding Intersectionality
Intersectionality recognizes that individuals experience multiple forms of oppression simultaneously, and that these forms of oppression intersect and compound each other. By examining the intersectionalities of oppression in cultural texts, readers can gain a deeper understanding of how texts reflect and shape societal norms and values.
4. The Role of the Reader in Shaping Meaning

Tyson's critical theory also highlights the role of the reader in shaping meaning. She argues that readers bring their own experiences, biases, and cultural backgrounds to the text, and that these factors shape their interpretation of the text.
Understanding Reader Response
Reader response theory recognizes that readers are active participants in the creation of meaning, rather than passive recipients of information. By examining the ways in which readers respond to texts, scholars can gain a deeper understanding of how texts shape and reflect societal norms and values.
5. The Importance of Critical Pedagogy

Finally, Tyson's critical theory emphasizes the importance of critical pedagogy in teaching and learning. Critical pedagogy involves teaching students to think critically about cultural texts and to recognize the power dynamics and ideological messages that underlie them.
Understanding Critical Pedagogy
Critical pedagogy involves creating a learning environment that encourages students to question and challenge dominant ideologies and power structures. By teaching students to think critically about cultural texts, educators can empower them to become active participants in shaping societal norms and values.
Gallery of Critical Theory Images
What is critical theory?
+Critical theory is a philosophical approach that critiques social and political power structures.
What is the importance of contextualization in critical theory?
+Contextualization is important in critical theory because it recognizes that texts must be analyzed within their historical, social, and cultural contexts to uncover their underlying power dynamics and ideological messages.
What is intersectionality in critical theory?
+Intersectionality refers to the idea that different forms of oppression, such as racism, sexism, and homophobia, intersect and overlap to create complex and nuanced systems of oppression.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of Lois Tyson's critical theory and its key takeaways. By applying these concepts to your own analysis of cultural texts, you can gain a more nuanced understanding of the power dynamics and ideological messages that shape our society.
