Intro
Delve into the intricacies of What Remains in the Gray Zone Explained, a thought-provoking exploration of moral ambiguity, ethics, and decision-making. Discover how the gray zone affects personal and professional life, and learn strategies for navigating uncertainty. Uncover the psychological and philosophical underpinnings of this complex concept.
The gray zone is a term used to describe a state of uncertainty, ambiguity, or confusion that can arise in various aspects of life, including personal relationships, work, and even international conflicts. It refers to a situation where the boundaries, rules, or expectations are unclear, leaving individuals or parties uncertain about how to navigate or respond. In this article, we will delve into the concept of the gray zone, its characteristics, and its implications in different contexts.
What is the Gray Zone?

The gray zone is a metaphorical space where the usual norms, rules, or expectations are suspended or unclear. It is a state of limbo, where individuals or parties are uncertain about how to behave, react, or make decisions. The gray zone can arise due to various factors, such as ambiguity, uncertainty, or conflicting information. In personal relationships, the gray zone might manifest as mixed signals, unclear boundaries, or unspoken expectations. In professional settings, it could be a lack of clear communication, conflicting priorities, or uncertain roles.
Characteristics of the Gray Zone
The gray zone is characterized by several key features:
- Ambiguity: The gray zone is marked by a lack of clear information, guidelines, or expectations.
- Uncertainty: Individuals or parties are uncertain about how to navigate or respond to the situation.
- Conflicting information: There may be conflicting signals, messages, or priorities that contribute to the ambiguity.
- Lack of clear boundaries: The gray zone often involves unclear or shifting boundaries, making it difficult to determine what is acceptable or expected.
- Emotional complexity: The gray zone can be emotionally charged, leading to feelings of anxiety, confusion, or frustration.
Navigating the Gray Zone

Navigating the gray zone requires a combination of critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and effective communication. Here are some strategies for navigating the gray zone:
- Seek clarity: Attempt to gather more information or clarify expectations to reduce ambiguity.
- Communicate effectively: Open and honest communication can help to resolve misunderstandings and establish clear boundaries.
- Set clear priorities: Establishing clear priorities can help to navigate conflicting demands or expectations.
- Be adaptable: The gray zone often requires flexibility and adaptability, as circumstances may change or evolve.
- Practice emotional regulation: Managing emotions is essential in the gray zone, as it can be emotionally complex and challenging.
Implications of the Gray Zone
The gray zone can have significant implications in various contexts, including:
- Personal relationships: The gray zone can lead to misunderstandings, conflict, or feelings of uncertainty in personal relationships.
- Professional settings: The gray zone can impact productivity, morale, or decision-making in professional settings.
- International conflicts: The gray zone can contribute to escalating conflicts or reducing diplomatic efforts.
Real-Life Examples of the Gray Zone
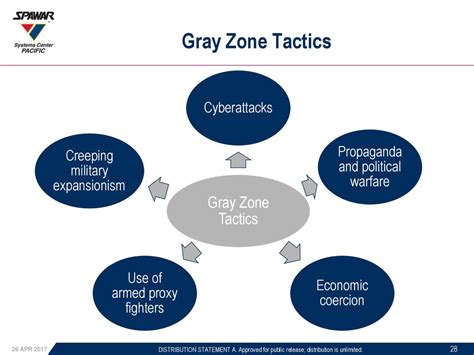
The gray zone can manifest in various real-life scenarios, such as:
- Mixed signals in dating: A person may send mixed signals, making it unclear whether they are interested in a romantic relationship or not.
- Unclear expectations at work: An employee may be uncertain about their role or responsibilities, leading to confusion or mistakes.
- International diplomacy: The gray zone can arise in international conflicts, where the rules of engagement or boundaries are unclear.
Benefits of Embracing the Gray Zone
While the gray zone can be challenging, it also offers opportunities for growth, learning, and innovation. By embracing the gray zone, individuals can:
- Develop critical thinking: The gray zone requires critical thinking and problem-solving, which can enhance cognitive abilities.
- Improve emotional intelligence: Navigating the gray zone can help individuals develop emotional intelligence and empathy.
- Foster creativity: The gray zone can stimulate creative thinking and innovation, as individuals seek to find new solutions.
Conclusion: Embracing the Gray Zone
The gray zone is a complex and multifaceted concept that can arise in various aspects of life. By understanding its characteristics and implications, individuals can develop strategies for navigating the gray zone effectively. While it can be challenging, the gray zone also offers opportunities for growth, learning, and innovation. By embracing the gray zone, individuals can develop critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and creativity, leading to personal and professional success.
Gray Zone Image Gallery





What is the gray zone?
+The gray zone refers to a state of uncertainty, ambiguity, or confusion that can arise in various aspects of life, including personal relationships, work, and even international conflicts.
What are the characteristics of the gray zone?
+The gray zone is characterized by ambiguity, uncertainty, conflicting information, lack of clear boundaries, and emotional complexity.
How can individuals navigate the gray zone effectively?
+Individuals can navigate the gray zone by seeking clarity, communicating effectively, setting clear priorities, being adaptable, and practicing emotional regulation.
