Intro
Learn how to convert 1 atomic mass unit (amu) to kilograms easily with our step-by-step guide. Discover the atomic mass definition, conversion formula, and calculate amu to kg, grams, and milligrams. Understand the difference between atomic mass and molecular weight with our informative article.
The concept of converting atomic mass units (amu) to kilograms may seem daunting, but it's actually quite straightforward. In this article, we'll explore the importance of understanding this conversion, its applications, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to do it easily.
Understanding Atomic Mass Units (amu)
Atomic mass units (amu) are a unit of mass used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. It's defined as one-twelfth the mass of a carbon-12 atom. The amu is widely used in chemistry and physics to calculate the mass of atoms and molecules. However, when working with larger quantities of matter, it's often necessary to convert amu to more familiar units like kilograms.
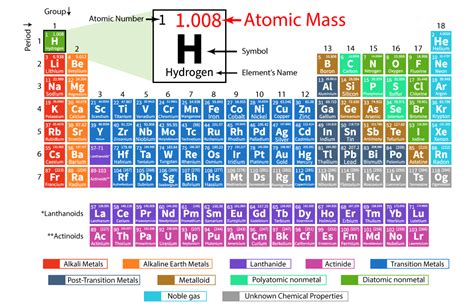
The Importance of Converting amu to Kilograms
Converting amu to kilograms is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. For instance, when calculating the mass of a substance in a laboratory setting, it's often necessary to convert the mass from amu to kilograms to ensure accurate measurements. Moreover, in industrial applications, converting amu to kilograms is essential for scaling up production processes.
Applications of amu to Kilogram Conversion
The conversion of amu to kilograms has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Converting amu to kilograms is essential for calculating the mass of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
- Physics: In physics, converting amu to kilograms is necessary for calculating the mass of particles and objects in various experiments.
- Engineering: In engineering, converting amu to kilograms is crucial for designing and scaling up production processes.
How to Convert 1 amu to Kilograms Easily
Converting 1 amu to kilograms is relatively simple. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Understand the conversion factor: 1 amu is equal to 1.66053904 × 10^-27 kilograms.
- Multiply the amu value by the conversion factor: Multiply 1 amu by the conversion factor (1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg/amu).
- Calculate the result: Perform the calculation to get the result in kilograms.
The result is approximately 1.66053904 × 10^-27 kilograms.
Practical Examples and Statistical Data
To illustrate the conversion process, let's consider a few examples:
- Example 1: Convert 5 amu to kilograms.
- Multiply 5 amu by the conversion factor (1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg/amu).
- Calculate the result: 5 × 1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg ≈ 8.3026952 × 10^-27 kg.
- Example 2: Convert 10 amu to kilograms.
- Multiply 10 amu by the conversion factor (1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg/amu).
- Calculate the result: 10 × 1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg ≈ 1.66053904 × 10^-26 kg.
These examples demonstrate how to convert amu to kilograms using the conversion factor.
amu to Kilogram Conversion Image Gallery





Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Converting 1 amu to kilograms is a straightforward process that requires understanding the conversion factor and performing a simple calculation. This conversion is essential in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can easily convert amu to kilograms and perform calculations with confidence.

We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the conversion factor for amu to kilograms?
+The conversion factor for amu to kilograms is 1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg/amu.
How do I convert 1 amu to kilograms?
+Multiply 1 amu by the conversion factor (1.66053904 × 10^-27 kg/amu) to get the result in kilograms.
What are some practical applications of converting amu to kilograms?
+Converting amu to kilograms has applications in chemistry, physics, and engineering, including calculating the mass of reactants and products in chemical reactions, calculating the mass of particles and objects in physics, and designing and scaling up production processes in engineering.
