Intro
Optimize Army retention with 5 crucial control points. Discover how to leverage career progression, compensation and benefits, education and training, and family support to boost soldier retention rates. Learn how to implement effective retention strategies, overcome challenges, and improve overall unit readiness and cohesion. Enhance your Armys ability to retain top talent.
The United States Army faces a significant challenge in retaining its soldiers. With the ever-present threat of terrorism, the importance of maintaining a skilled and experienced military force cannot be overstated. The Army's retention control points are crucial in determining which soldiers are allowed to continue serving and which are discharged. In this article, we will examine the 5 key Army retention control points and explore their significance in ensuring the Army maintains a strong and capable fighting force.
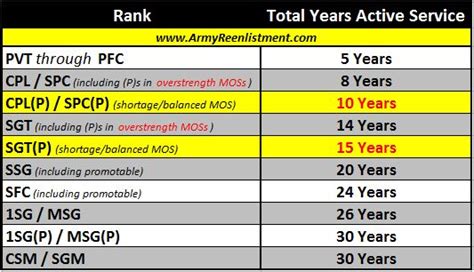
Understanding Army Retention Control Points
Before delving into the specifics of the 5 key Army retention control points, it is essential to understand what they are and why they are important. Army retention control points are designated periods in a soldier's career when their performance, behavior, and potential for future service are evaluated. These evaluations determine whether a soldier is allowed to continue serving in the Army or is discharged.
1. Initial Entry Training (IET)
The first retention control point occurs during Initial Entry Training (IET), also known as Basic Combat Training (BCT). During IET, new recruits are assessed on their ability to adapt to the Army's standards and expectations. Recruits who fail to meet these standards may be discharged from the Army.

2. Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
The second retention control point occurs after Advanced Individual Training (AIT), which is specialized training that follows IET. During AIT, soldiers are evaluated on their ability to learn and apply the skills required for their specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS). Soldiers who fail to meet the standards of their MOS may be reclassified or discharged.
3. First Term
The third retention control point occurs at the end of a soldier's first term of service, typically after 3-4 years. During this period, soldiers are evaluated on their overall performance, including their duty performance, physical fitness, and adherence to Army standards. Soldiers who fail to meet these standards may be denied reenlistment or be discharged.

4. Mid-Career
The fourth retention control point occurs mid-career, typically around the 10-15 year mark. During this period, soldiers are evaluated on their potential for future service and their ability to take on more senior roles. Soldiers who fail to demonstrate this potential may be considered for separation or retirement.
5. End of Service
The fifth and final retention control point occurs at the end of a soldier's service, typically after 20-30 years. During this period, soldiers are evaluated on their overall performance and their eligibility for retirement. Soldiers who fail to meet these standards may be denied retirement benefits or be discharged.

Gallery of Army Retention Control Points
Army Retention Control Points Image Gallery










FAQs
What is the purpose of Army retention control points?
+The purpose of Army retention control points is to evaluate a soldier's performance, behavior, and potential for future service to determine whether they are allowed to continue serving in the Army.
How many retention control points are there in the Army?
+There are 5 key retention control points in the Army, which occur during Initial Entry Training, Advanced Individual Training, the end of the first term, mid-career, and the end of service.
What happens if a soldier fails to meet the standards at a retention control point?
+If a soldier fails to meet the standards at a retention control point, they may be discharged from the Army, reclassified, or denied reenlistment or retirement benefits.
In conclusion, the 5 key Army retention control points play a crucial role in determining which soldiers are allowed to continue serving in the Army. By understanding these control points, soldiers can better prepare themselves for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with Army retention control points in the comments below.
