Intro
Discover the ins and outs of telegraphic speech, a unique communication style characterized by brief, concise language. Learn the definition, examples, and significance of telegraphic speech, including its relation to telegraphic language, syntax, and cognitive development. Understand how this distinctive speech pattern is used in various contexts, from child language acquisition to written communication.
Telegraphic speech is a type of language development in children where they use short, simplified sentences to communicate. This stage is characterized by the use of basic vocabulary and sentence structures, often with a focus on conveying the most essential information.
Telegraphic speech is a normal part of language development, typically occurring between the ages of two and three years old. During this stage, children begin to use short sentences, often omitting grammatical markers such as articles, auxiliary verbs, and prepositions. This type of speech is called "telegraphic" because it resembles the concise language used in telegrams, where unnecessary words are omitted to convey the main message quickly and efficiently.
Here are some examples of telegraphic speech:
- "Want juice" (instead of "I want some juice")
- "Ball gone" (instead of "The ball is gone")
- "Me go outside" (instead of "I want to go outside")
In these examples, the child is using simple vocabulary and sentence structures to convey their message. They are omitting unnecessary words and focusing on the most essential information.
Telegraphic speech is an important milestone in language development, as it shows that the child is beginning to understand the relationship between words and meaning. It also indicates that the child is developing their ability to communicate effectively and efficiently.
Characteristics of Telegraphic Speech

Telegraphic speech has several distinct characteristics, including:
- Simple vocabulary: Children use basic words and phrases to convey their message.
- Short sentences: Sentences are typically short and concise, often with only a few words.
- Omission of grammatical markers: Children may omit articles, auxiliary verbs, and prepositions to convey the most essential information.
- Focus on content words: Children focus on using content words, such as nouns and verbs, to convey meaning.
- Limited use of pronouns: Children may use limited pronouns, such as "me" instead of "I".
Examples of Telegraphic Speech
Here are some more examples of telegraphic speech:
- "Mama go" (instead of "Mommy is going")
- "Want cookie" (instead of "I want a cookie")
- "Ball roll" (instead of "The ball is rolling")
These examples illustrate the characteristic features of telegraphic speech, including simple vocabulary, short sentences, and the omission of grammatical markers.
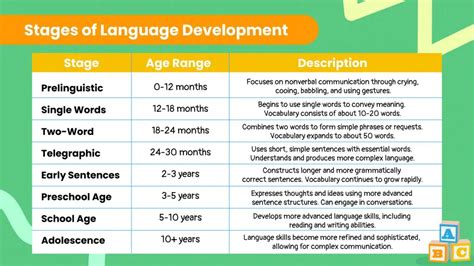
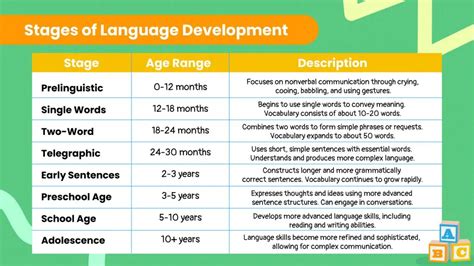
Developmental Stage of Telegraphic Speech

Telegraphic speech typically occurs between the ages of two and three years old, although this can vary depending on the individual child. During this stage, children are learning to use language to communicate effectively and efficiently.
Here are some key milestones in the development of telegraphic speech:
- 12-18 months: Children begin to use simple gestures and vocalizations to communicate.
- 18-24 months: Children start to use simple words and phrases, such as "mama" or "dada".
- 2-3 years: Children enter the telegraphic speech stage, using short sentences and omitting grammatical markers.
- 3-4 years: Children begin to use more complex sentences and grammatical structures, such as verb tenses and pronouns.
Importance of Telegraphic Speech
Telegraphic speech is an important milestone in language development, as it shows that the child is beginning to understand the relationship between words and meaning. It also indicates that the child is developing their ability to communicate effectively and efficiently.
Telegraphic speech is also an important precursor to more complex language skills, such as:
- Syntax: The arrangement of words to form sentences.
- Semantics: The meaning of words and sentences.
- Pragmatics: The use of language in social contexts.
By understanding telegraphic speech, parents and caregivers can support children's language development and help them build a strong foundation for future language skills.
Gallery of Telegraphic Speech




Frequently Asked Questions
What is telegraphic speech?
+Telegraphic speech is a type of language development in children where they use short, simplified sentences to communicate.
What are the characteristics of telegraphic speech?
+Telegraphic speech is characterized by simple vocabulary, short sentences, omission of grammatical markers, focus on content words, and limited use of pronouns.
What is the developmental stage of telegraphic speech?
+Telegraphic speech typically occurs between the ages of two and three years old, although this can vary depending on the individual child.
In conclusion, telegraphic speech is an important milestone in language development, marking the beginning of children's ability to communicate effectively and efficiently. By understanding the characteristics, developmental stage, and importance of telegraphic speech, parents and caregivers can support children's language development and help them build a strong foundation for future language skills.
