Intro
Discover the B-37 Bomber, a forgotten marvel of WWII aviation history. Learn about its development, features, and impact on the war effort. Explore the aircrafts innovative design, technical specifications, and combat performance, alongside other notable bombers of the era, such as the B-29 and B-24.
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress, the North American B-25 Mitchell, and the Consolidated B-24 Liberator are some of the most iconic bombers of World War II. However, there was another bomber that played a significant role in the war, yet remains largely forgotten in the annals of history - the Douglas B-37. In this article, we will delve into the story of the B-37, its development, features, and operations, and explore why it remains a relatively unknown chapter in the history of WWII aviation.
Development and Design
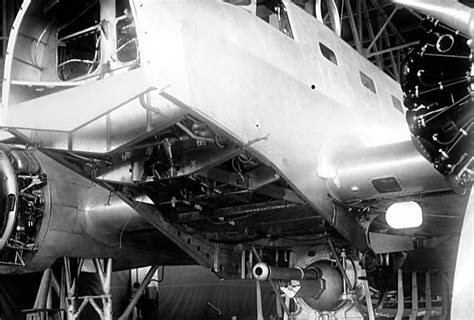
The Douglas B-37 was a medium bomber designed by the Douglas Aircraft Company in the late 1930s. The aircraft was intended to replace the Douglas B-23 Dragon, which was the primary medium bomber of the US Army Air Corps (USAAC) at the time. The B-37 was designed to be faster, more maneuverable, and have a longer range than its predecessor.
The B-37 had a sleek and streamlined fuselage, with a distinctive curved wing design. It was powered by two Wright R-1820 radial engines, which provided a top speed of around 320 mph. The aircraft had a crew of four, consisting of a pilot, co-pilot, navigator, and bombardier.
Armament and Defensive Features
The B-37 was armed with four.50-caliber machine guns, two of which were mounted in the nose turret, and two in the dorsal turret. The aircraft also had a bomb bay capable of carrying up to 4,000 pounds of ordnance.
In terms of defensive features, the B-37 had a number of innovations, including a gyro-stabilized gun sight and a semi-automatic bomb release system. The aircraft also had a unique " crawlspace" bomb bay, which allowed the bombardier to access the bomb bay from the navigator's compartment.
Operational History

The B-37 entered service with the USAAC in 1940, and was initially used for training and reconnaissance missions. However, with the outbreak of World War II, the B-37 was pressed into combat service, operating in North Africa, Italy, and the Pacific.
Despite its relatively small numbers, the B-37 played a significant role in several key campaigns, including the Battle of El Alamein and the invasion of Sicily. The aircraft's speed and maneuverability made it an effective fighter-bomber, and it was often used to attack enemy airfields and troop concentrations.
The B-37's Finest Hour
One of the most notable operations undertaken by the B-37 was the bombing of the German airfield at Tobruk, Libya. On November 17, 1942, a formation of 12 B-37s attacked the airfield, destroying or damaging over 100 enemy aircraft. The raid was a significant success, and marked one of the few occasions where the B-37 was used in a large-scale bombing operation.
Decline and Legacy

Despite its successes, the B-37 was eventually phased out of service in favor of more modern aircraft, such as the B-25 Mitchell and the B-26 Marauder. The last B-37 was retired from service in 1945.
The B-37's legacy is somewhat mixed. While it played an important role in several key campaigns, it was ultimately overshadowed by other, more famous aircraft. However, the B-37 remains an interesting footnote in the history of WWII aviation, and a testament to the innovative spirit of the Douglas Aircraft Company.
Why Was the B-37 Forgotten?
There are several reasons why the B-37 was largely forgotten in the aftermath of World War II. One reason is that the aircraft was not as widely produced or used as other bombers, such as the B-17 or the B-24. Additionally, the B-37's role in the war was often overshadowed by other, more glamorous aircraft.
However, another reason for the B-37's relative obscurity may be due to the fact that it did not have a particularly distinctive or memorable name. Unlike the "Flying Fortress" or the "Liberator," the B-37 did not have a nickname that stuck in the popular imagination.
Gallery of B-37 Images
B-37 Bomber Image Gallery










What was the primary role of the B-37?
+The primary role of the B-37 was as a medium bomber, used for attacking enemy airfields, troop concentrations, and other strategic targets.
How many B-37s were produced?
+A total of 455 B-37s were produced by the Douglas Aircraft Company.
What was the B-37's top speed?
+The B-37 had a top speed of around 320 mph.
We hope this article has shed some light on the fascinating story of the Douglas B-37, a forgotten marvel of WWII aviation history. Whether you're a historian, an aviation enthusiast, or simply someone interested in learning more about the war, we encourage you to share this article with others and keep the memory of the B-37 alive.
